A point cloud classification downsampling and registration method for cultural relics based on curvature features
-
摘要:
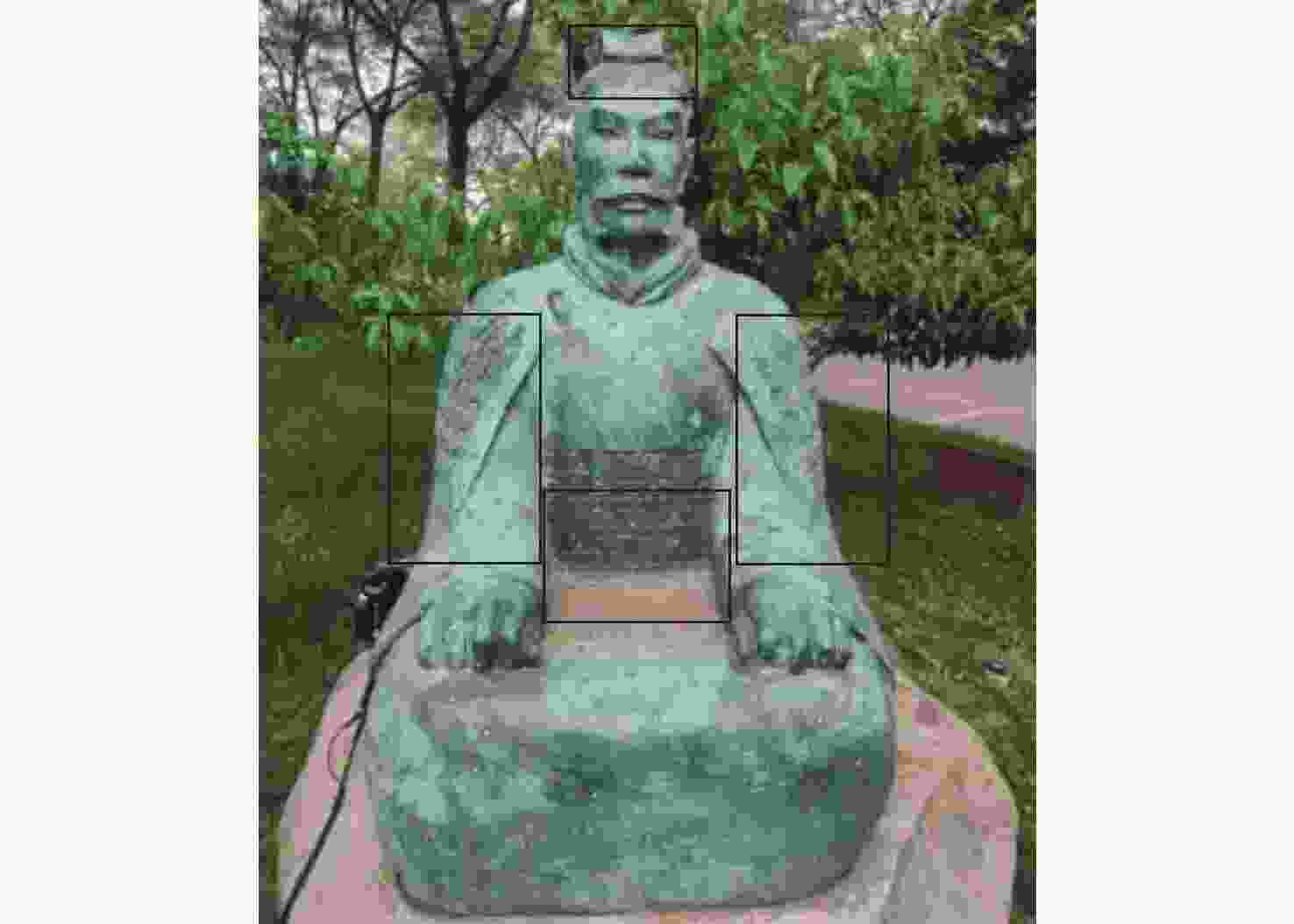
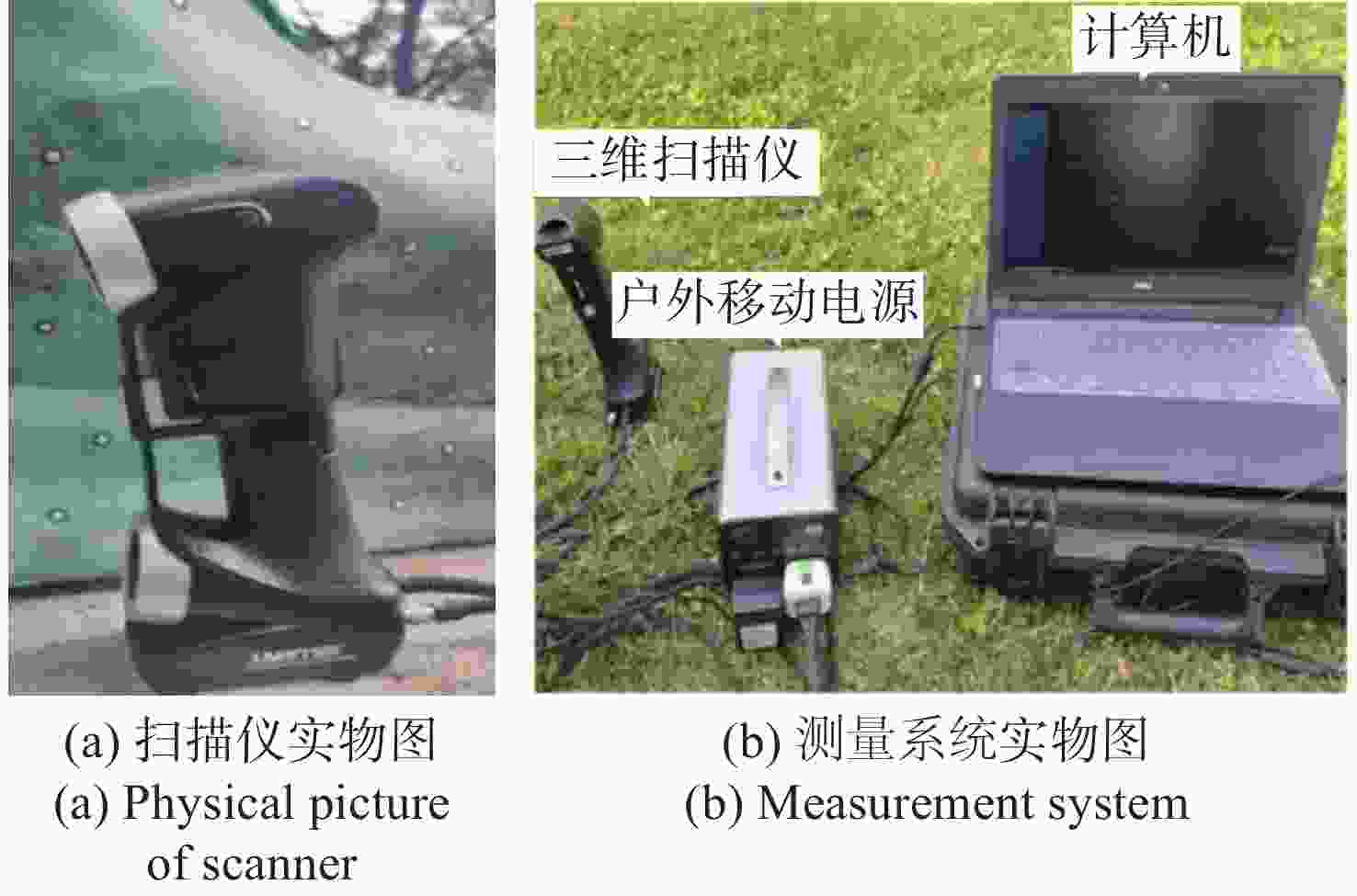
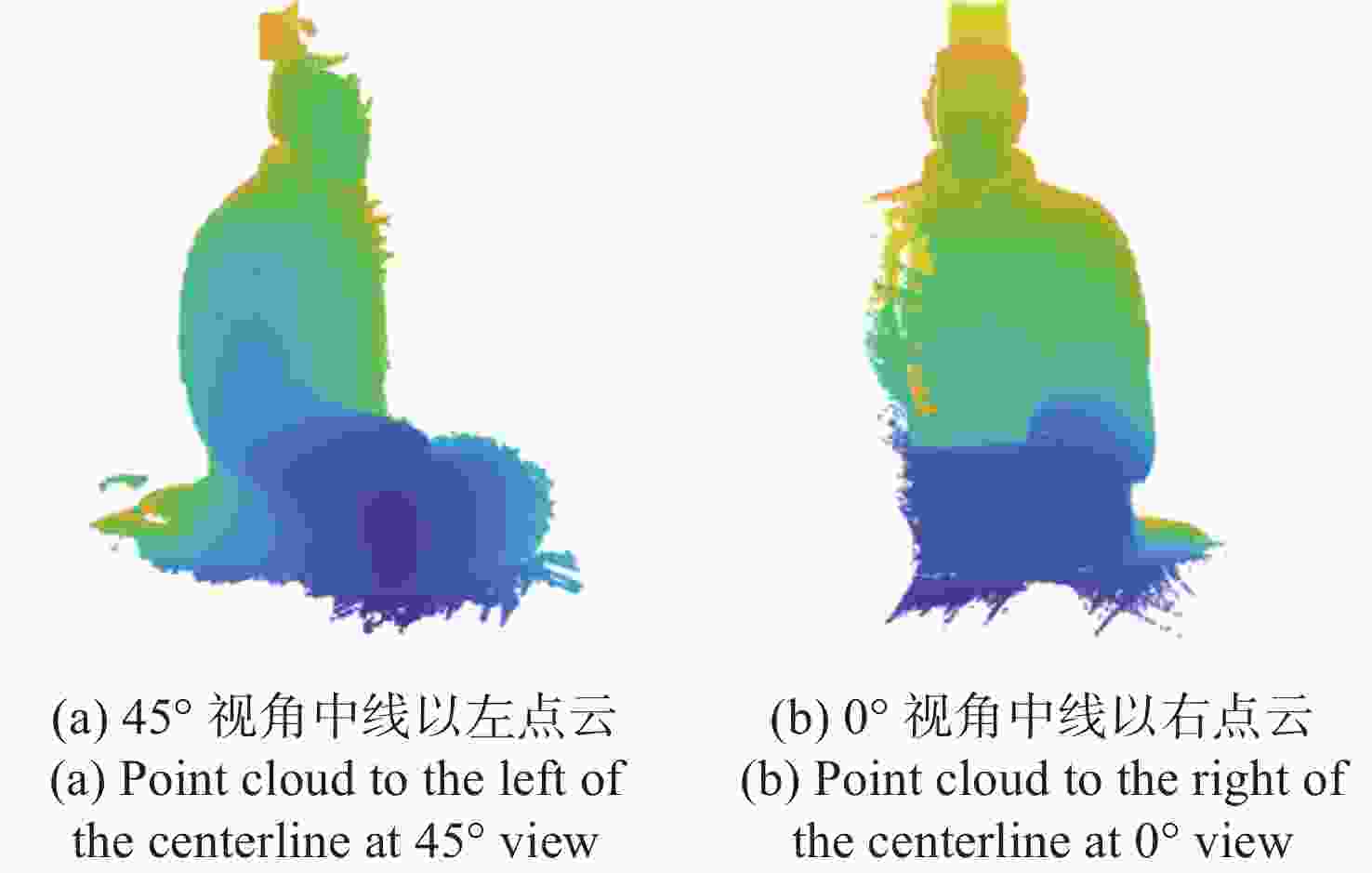
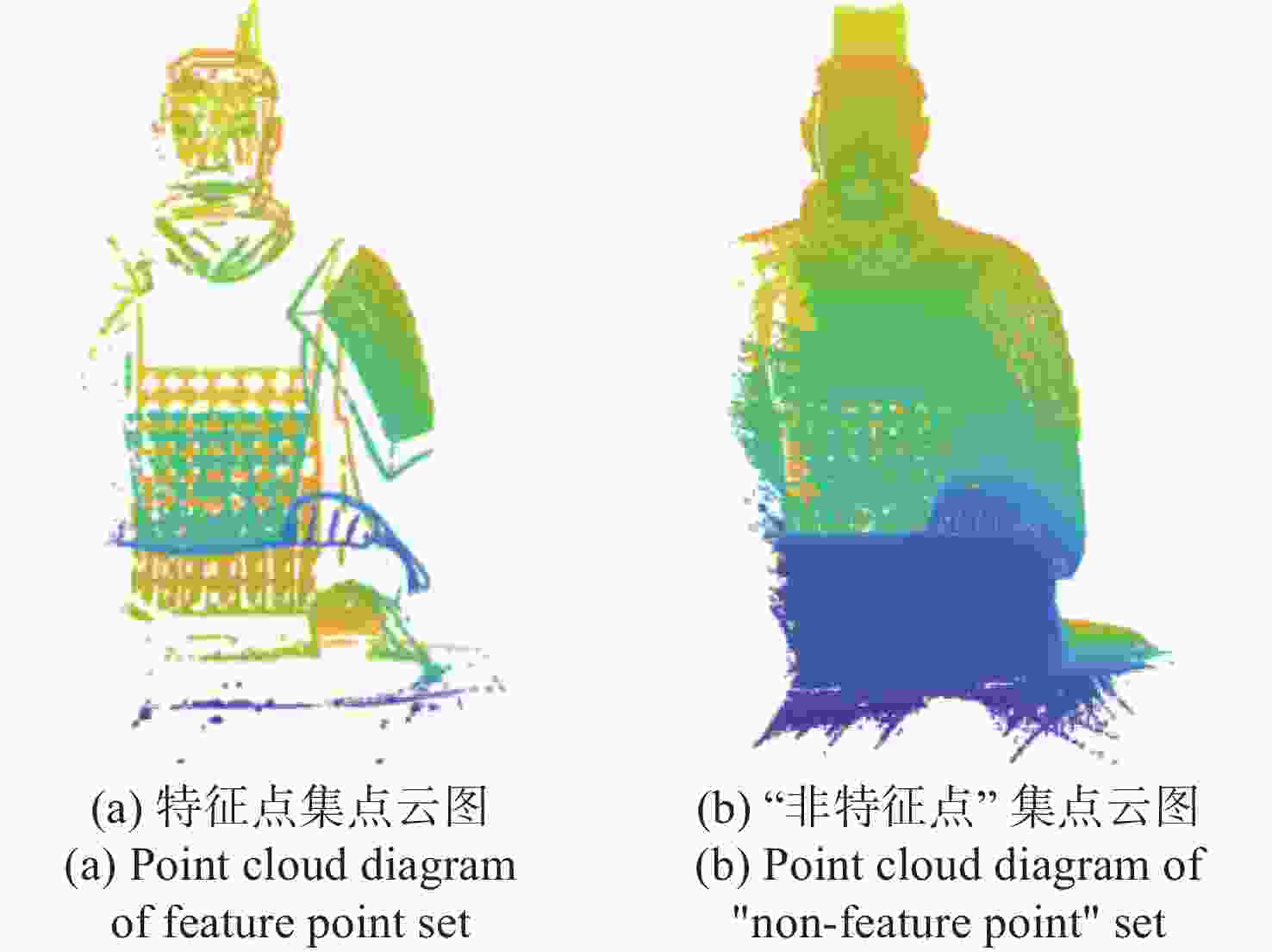
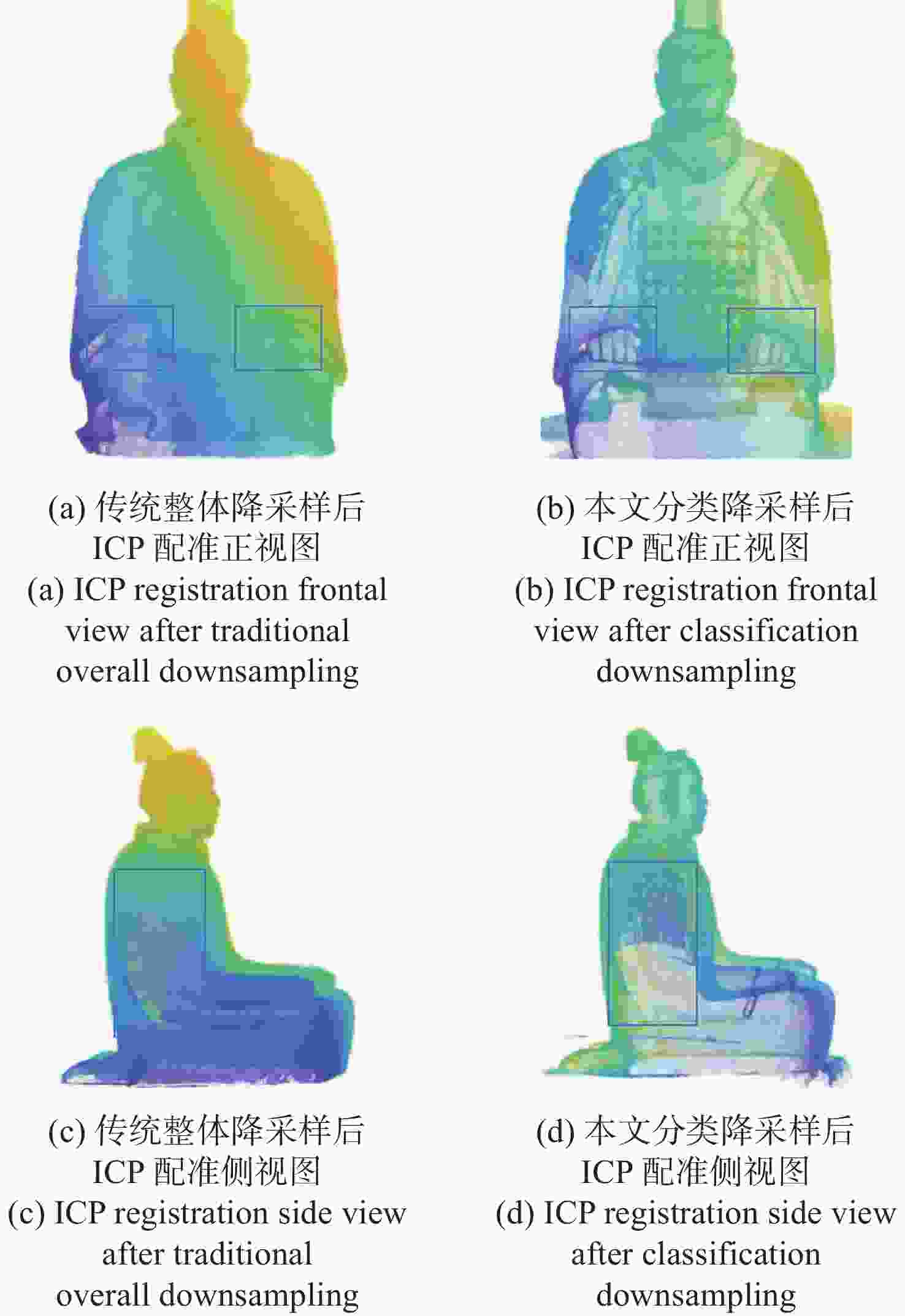
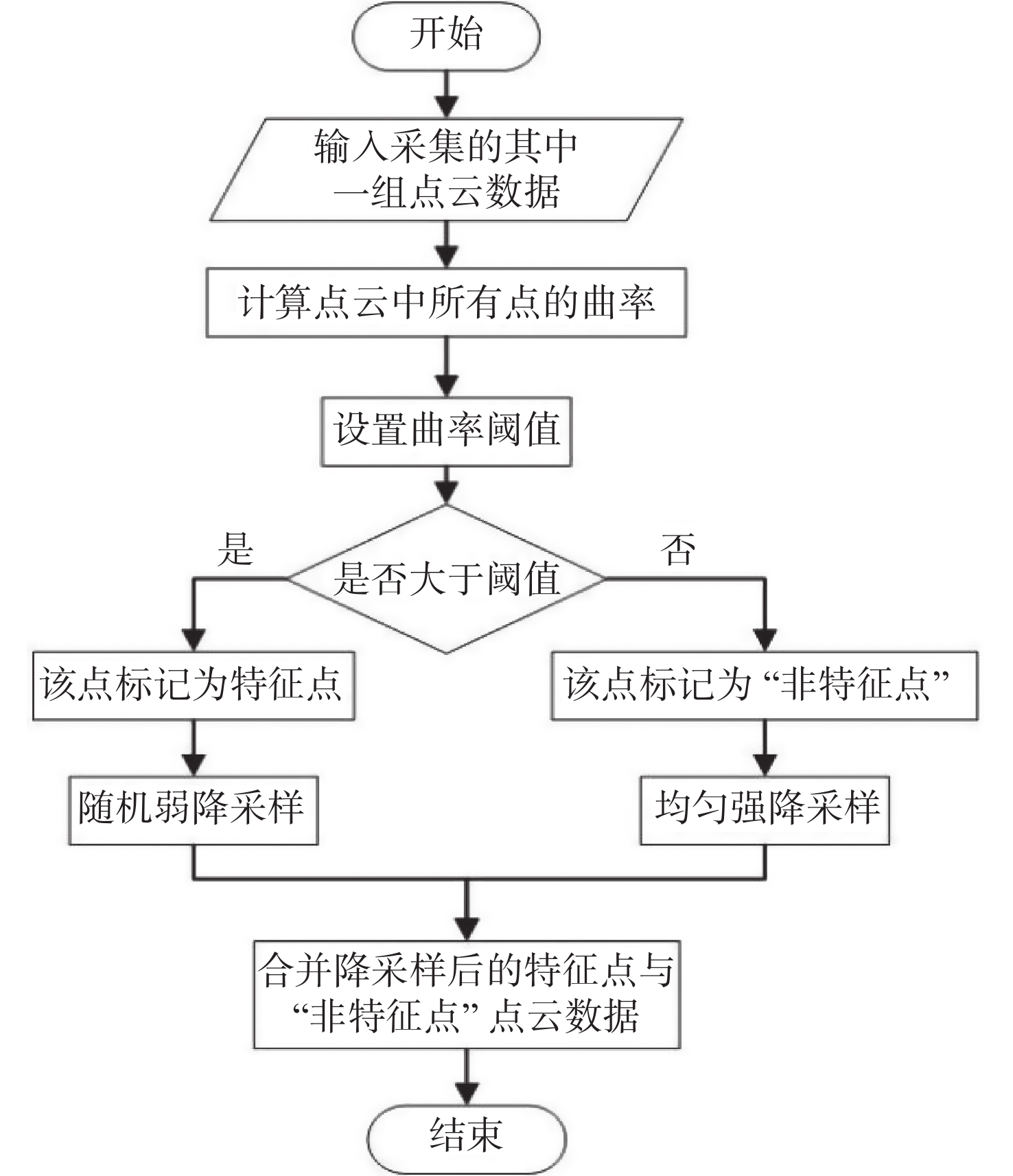
三维重构是文物数字化的关键技术,其中三维点云配准精度是评估重构质量优劣的重要指标之一。实际采样中,文物点云细节信息繁多,传统降采样后易出现细节缺失从而影响配准精度。为了解决这一问题,本文提出了一种基于曲率特征的文物点云分类降采样与配准方法。首先,通过线性矩阵金宝搏188软件怎么用 测量获取文物的三维点云数据。其次,计算所有点的曲率值,并设置曲率阈值进行点云分类,不同点集按照其特征属性进行不同权重的降采样,从而最大限度地保留点云的形态特征和细节信息。最后,通过求解刚性变换模型实现点云配准。点云配准前的降采样处理后点云数据降至原始点云的1/3,与传统的整体降采样ICP方法相比,平均距离从0.89 mm约降至0.59 mm,标准偏差从0.29 mm约降至0.18 mm。在降低点云数据的同时也保证了配准的精度,适用于不同类型的文物点云数据。
Abstract:3D reconstruction is crucial for digitization of cultural relics, and the accuracy of 3D point cloud registration is a significant metric for evaluating the reconstruction quality. In practice, cultural relics point cloud data includes numerous details, and using conventional downsampling methods may result in the loss of such details, thereby affecting registration accuracy. We propose a point cloud classification downsampling and registering method for cultural relics based on curvature features. First, 3D point clouds data of cultural relics are obtained using linear matrix laser measurement. Next, the curvature values of all points are calculated, and a curvature threshold is set for point cloud classification. Different point sets are carried out downsampling with different weights according to their feature attributes to retain the shape features and details of the point cloud as much as possible. Finally, point cloud registration is achieved through calculating the rigid transformation model. Compared to the traditional global downsampling ICP method, the point cloud data of the downsampling processing before point cloud registration reduces to 1/3 of the original size. The average distance decreases from approximately 0.89 mm to 0.59 mm, while the standard deviation decreases from about 0.29 mm to 0.18 mm. This approach guarantees the accuracy of downsampling and registration and is applicable to various cultural relics point cloud data.
-
表 1 本文分类降采样数据
Table 1. The classification downsampling data of this paper
原始点云数量 配准后点云数量 平均距离/mm 标准偏差/mm 1950581 422423 152816 575239 表 2 仿真铜像点云配准实验过程数据分析
Table 2. Experiment process data analysis of point cloud registration for simulated copper statue
方法 原始点云
数量配准后点云
数量平均距离
/mm标准偏差
/mm传统整体
降采样后3471705 985621 0.891086 0.296167 本文分类
降采样后3471705 981584 0.591977 0.180786 -
[1] 阎春生, 黄晨, 韩松涛, 等. 古代纸质文物科学检测技术综述[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(5):936-964. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0010YAN CH SH, HUANG CH, HAN S T, et al. Review on scientific detection technologies for ancient paper relics[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(5): 936-964. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0010 [2] 张瑞, 骆岩林, 周明全, 等. 文物数字化的关键技术[J]. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版),2007,43(2):150-153.ZHANG R, LUO Y L, ZHOU M Q, et al. The key technology in digital cultural relics[J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science), 2007, 43(2): 150-153. (in Chinese). [3] 陈辉, 马世伟, NUECHTER A. 基于金宝搏188软件怎么用 扫描和SFM的非同步点云三维重构方法[J]. 仪器仪表学报,2016,37(5):1148-1157.CHEN H, MA SH W, NUECHTER A. Non-synchronous point cloud algorithm for 3D reconstruction based on laser scanning and SFM[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2016, 37(5): 1148-1157. (in Chinese). [4] 王蕊, 李俊山, 刘玲霞, 等. 基于几何特征的点云配准算法[J]. 华东理工大学学报(自然科学版),2009,35(5):768-773.WANG R, LI J SH, LIU L X, et al. Registration of point clouds based on geometric properties[J]. Journal of East China University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 35(5): 768-773. (in Chinese). [5] 张新荣, 王鑫, 王瑶, 等. 基于转动式二维金宝搏188软件怎么用 扫描仪和多传感器的三维重建方法[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(3):663-672. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0159ZHANG X R, WANG X, WANG Y, et al. 3D reconstruction method based on a rotating 2D laser scanner and multi-sensor[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(3): 663-672. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0159 [6] 杨鹏程, 杨朝, 孟杰, 等. 基于法向量和面状指数特征的文物点云棱界配准方法[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(3):654-662. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0156YANG P CH, YANG ZH, MENG J, et al. Aligning method for point cloud prism boundaries of cultural relics based on normal vector and faceted index features[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(3): 654-662. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0156 [7] 林森, 张强. 应用邻域点信息描述与匹配的点云配准[J]. 光学 精密工程,2022,30(8):984-997. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223008.0984LIN S, ZHANG Q. Point cloud registration using neighborhood point information description and matching[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(8): 984-997. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223008.0984 [8] ZHAO H, ZHANG Y J, ZHANG L, et al. Fast color point cloud registration based on virtual viewpoint image[J]. Frontiers in Physics, 2022, 10: 1026517. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2022.1026517 [9] 毕勇, 潘鸣奇, 张硕, 等. 三维点云数据超分辨率技术[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(2):210-223. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0176BI Y, PAN M Q, ZHANG SH, et al. Overview of 3D point cloud super-resolution technology[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(2): 210-223. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0176 [10] 伍济钢, 马佳康, 杨康, 等. 基于改进ICP的复杂机械零件测量点云配准方法[J]. 光电子·金宝搏188软件怎么用 ,2023,34(6):620-627. doi: 10.16136/j.joel.2023.06.0337WU J G, MA J K, YANG K, et al. Measurement point cloud registration method for complex mechanical parts based on improved ICP[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics·Laser, 2023, 34(6): 620-627. (in Chinese). doi: 10.16136/j.joel.2023.06.0337 [11] QIN H X, ZHANG Y CH, LIU ZH T, et al. Rigid registration of point clouds based on partial optimal transport[J]. Computer Graphics Forum, 2022, 41(6): 365-378. doi: 10.1111/cgf.14614 [12] ZHANG K X, CHEN H, WU H, et al. Point cloud registration method for maize plants based on conical surface fitting—ICP[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12(1): 6852. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-10921-6 [13] 张彬, 熊传兵. 基于体素下采样和关键点提取的点云自动配准[J]. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 与光电子学进展,2020,57(4):041008.ZHANG B, XIONG CH B. Automatic point cloud registration based on voxel downsampling and key point extraction[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(4): 041008. (in Chinese). [14] GARLAND M, HECKBERT P S. Surface simplification using quadric error metrics[C]. Proceedings of the 24th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, ACM, 1997: 209-216. [15] SU H, JAMPANI V, SUN D Q, et al. SPLATNet: sparse lattice networks for point cloud processing[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2018: 2530-2539. [16] 汪千金, 崔海华, 张益华, 等. 面向光学测量跨源点云的多尺度采样配准方法[J]. 光学学报,2022,42(10):1015002. doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.1015002WANG Q J, CUI H H, ZHANG Y H, et al. Multi-scale sampling registration method for optical measurement of cross-source point clouds[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2022, 42(10): 1015002. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.1015002 [17] LU J, WANG ZH, HUA B W, et al. Automatic point cloud registration algorithm based on the feature histogram of local surface[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(9): e0238802. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238802 [18] CHEN Y W, ZHOU L D, TANG Y, et al. Fast neighbor search by using revised k-d tree[J]. Information Sciences, 2019, 472: 145-162. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.09.012 [19] 金泽芬芬, 侯志强, 余旺盛, 等. 基于协方差矩阵的多特征融合跟踪算法[J]. 光学学报,2017,37(9):0915005. doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.0915005JIN Z F F, HOU ZH Q, YU W SH, et al. Multi-feature fusion tracking algorithm based on the covariance matrix[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2017, 37(9): 0915005. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.0915005 [20] ILEA I, BOMBRUN L, TEREBES R, et al. An M-estimator for robust centroid estimation on the manifold of covariance matrices[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(9): 1255-1259. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2016.2594149 [21] FU Y J, LI Z CH, DENG Y, et al. Pairwise registration for terrestrial laser scanner point clouds based on the covariance matrix[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 12(8): 788-798. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2021.1938734 [22] WANG X H, CHEN H W, WU L SH. Feature extraction of point clouds based on region clustering segmentation[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2020, 79(17-18): 11861-11889. doi: 10.1007/s11042-019-08512-1 [23] 李韦童, 邓念武. 一种预拼装钢构件的点云自动分割算法[J]. 武汉大学学报(工学版),2022,55(3):247-252. doi: 10.14188/j.1671-8844.2022-03-005LI W T, DENG N W. An automatic point cloud data segmentation algorithm for pre-assembled steel structures[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2022, 55(3): 247-252. (in Chinese). doi: 10.14188/j.1671-8844.2022-03-005 [24] 魏磊, 万帅, 王哲诚, 等. 面向点云无损压缩的快速细节层次优化方法[J]. 西安交通大学学报,2021,55(9):88-96.WEI L, WAN SH, WANG ZH CH, et al. Optimization method for level of detail of lossless point cloud compression[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2021, 55(9): 88-96. (in Chinese). [25] 郭培闪, 杜黎明. 运用Geomagic Studio实现点云数据的曲面重建及误差分析[J]. 地理信息世界,2015,22(1):57-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1586.2015.01.016GUO P SH, DU L M. Realized the surface reconstruction of point clouds and error analysis by using the Geomagic Studio[J]. Geomatics World, 2015, 22(1): 57-60. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1586.2015.01.016 [26] 戴静兰, 陈志杨, 叶修梓. ICP算法在点云配准中的应用[J]. 中国图象图形学报,2007,12(3):517-521.DAI J L, CHEN ZH Y, YE X Z. The application of ICP algorithm in point cloud alignment[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2007, 12(3): 517-521. (in Chinese). [27] SOUZA NETO P, MARQUES SOARES J, PEREIRA THÉ G A. Uniaxial partitioning strategy for efficient point cloud registration[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(8): 2887. doi: 10.3390/s22082887 -






 下载:
下载: