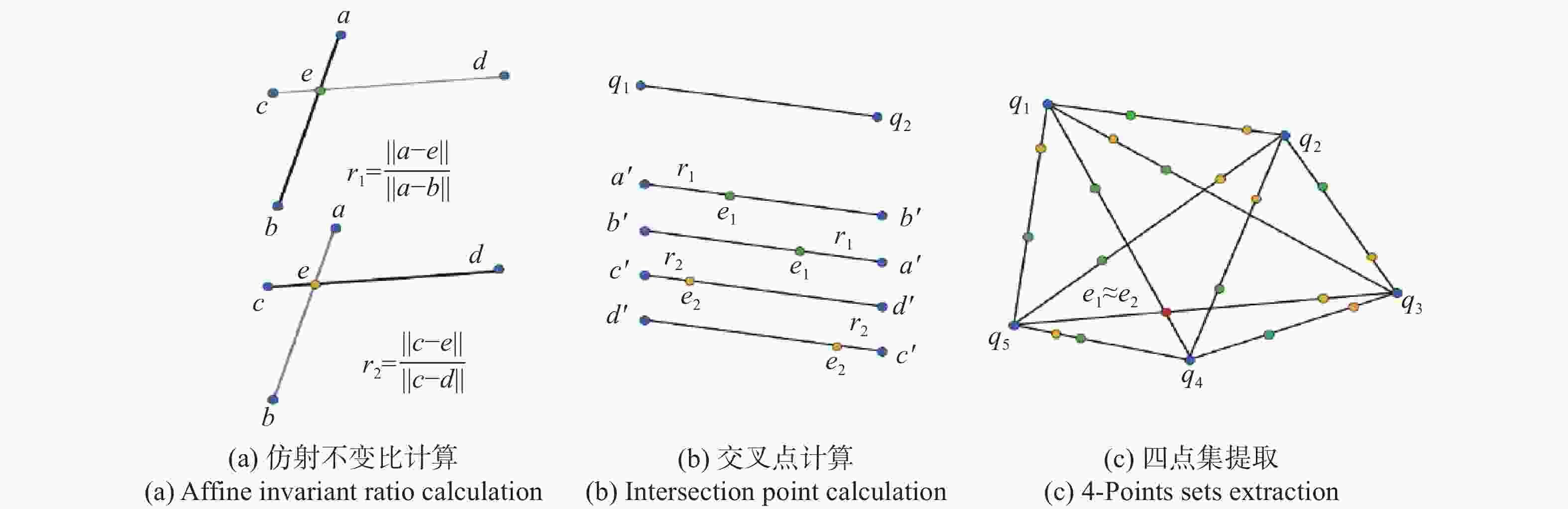
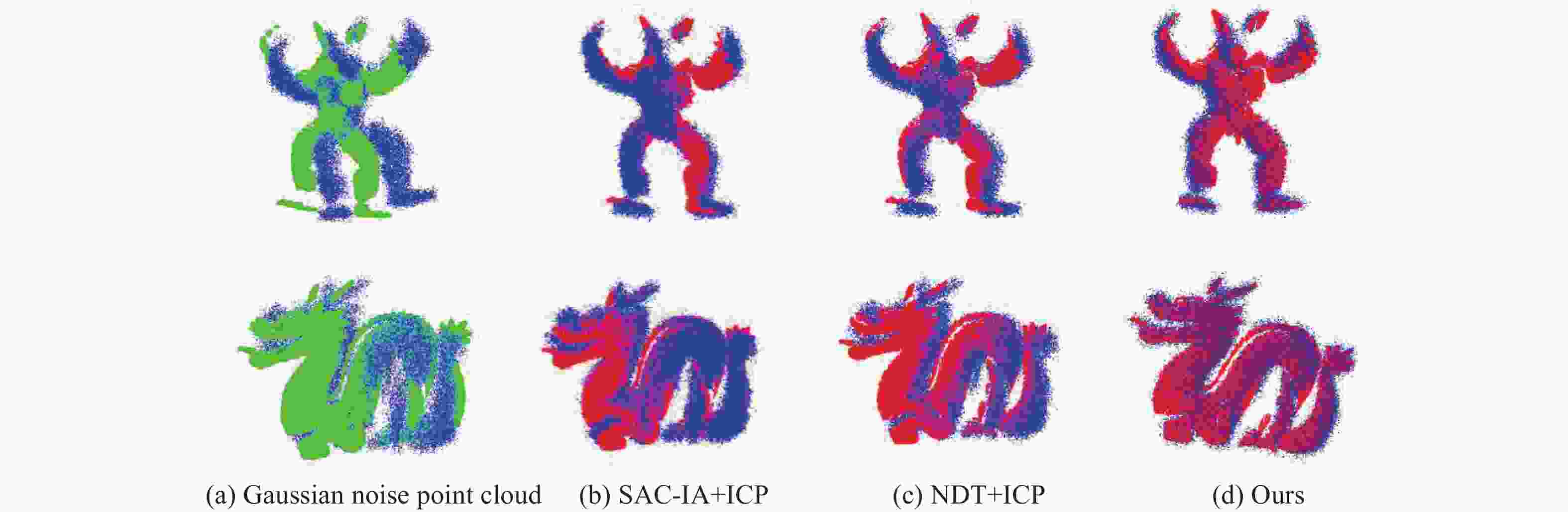
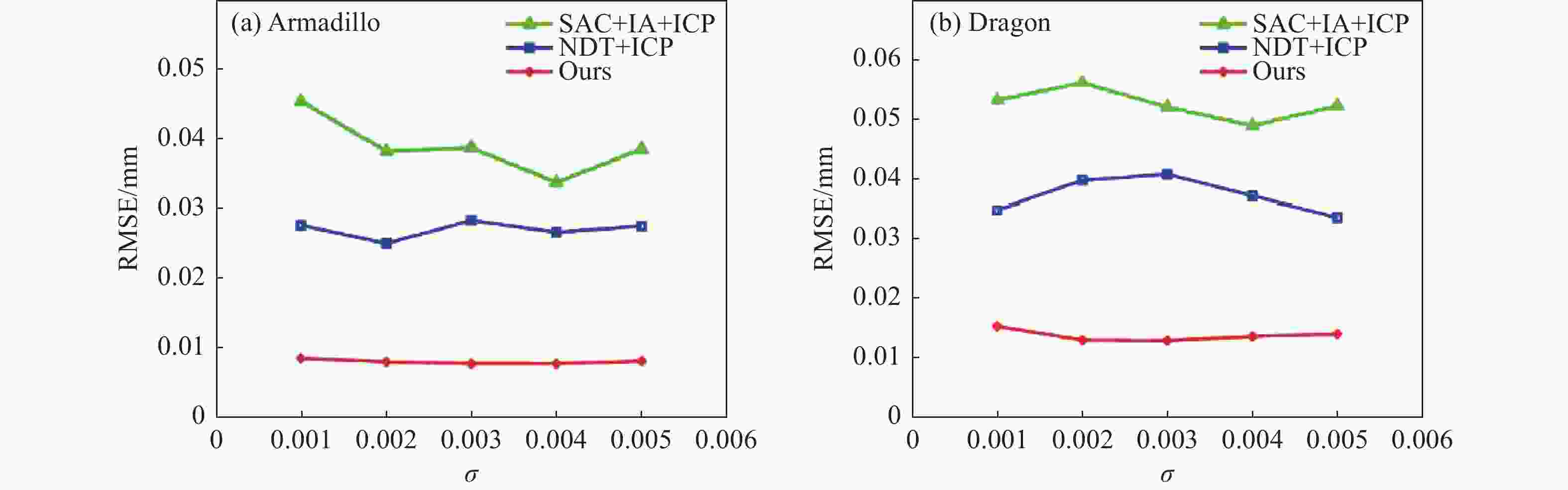
An improved point cloud registration method based on the point-by-point forward method
-
摘要:
点云配准是获取三维点云模型空间姿态的关键步骤,为了进一步提高点云配准的效率和准确性,提出了一种基于逐点前进法特征点提取的改进型点云配准方法。首先,利用逐点前进法快速提取点云特征点,在保留点云模型特征的同时大幅精简点云数量。然后,通过使用法向量约束改进的KN-4PCS算法进行粗配准,以实现源点云与目标点云的初步配准。最后,使用双向Kd-tree优化的LM-ICP算法完成精配准。实验结果显示:在斯坦福大学开放点云数据配准实验中,其平均误差较SAC-IA+ICP算法减少了约70.2%,较NDT+ICP算法减少了约49.6%,配准耗时分别减少约86.2%和81.9%,同时在引入不同程度的高斯噪声后仍能保持较高的精度和较低的耗时。在真实室内物体点云配准实验中,其平均配准误差为0.0742 mm,算法耗时平均为0.572 s。通过斯坦福开放数据与真实室内场景物体点云数据对比分析结果表明:本方法能够有效提高点云配准的效率、准确性和鲁棒性,为基于点云的室内目标识别与位姿估计奠定了良好的基础。
Abstract:We propose an improved point cloud registration method based on point-by-point forward feature point extraction to improve the efficiency and accuracy of point cloud registration. Firstly, the point-by-point forward method was used to quickly extract the point cloud feature points, significantly reducing the number of point clouds while retaining the characteristics of the point cloud model. Then, the improved KN-4PCS algorithm using normal vector constraints was coarsely registered to achieve the preliminary registration of the source point cloud and the target point cloud. Finally, the two-way Kd-tree optimized LM-ICP algorithm was used to complete the fine registration. In this paper, registration experiments were conducted on different point cloud data. In the registration experiment on Stanford University open point cloud data, the average error was reduced by about 70.2% compared with the SAC-IA+ICP algorithm, about 49.6% compared with the NDT+ICP algorithm, and the registration time was reduced by about 86.2% and 81.9%, respectively, while maintaining high accuracy and lower time consumption after introducing different degrees of Gaussian noise. In the point cloud registration experiment on real indoor objects, the average registration error was 0.0742 mm, and the average algorithm time was 0.572 s. The experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively improve the point cloud registration’s efficiency, accuracy, and robustness, thereby providing a solid foundation for indoor target recognition and pose estimation based on the point cloud.
-
Key words:
- point cloud registration /
- KN-4PCS /
- bidirectional Kd-tree /
- LM-ICP
-
表 1 深度相机参数
Table 1. RGB-D camera’s parameters
参数名称 数值 工作范围 0.6~8 m 深度 精度 l m: ±3 mm 视场角(FOV) H58.4 × V45.5° 分辨率@帧率 640 × 480@30 fps 视场角(FOV) H66.1° × 740.2° RGB 分辨率@帧率 640 × 480@30 fps UVC 支持 表 2 斯坦福点云配准定量分析结果
Table 2. Quantitative analysis results of Stanford point cloud data registration
Model SAC-IA+ICP NDT+ICP Ours RMSE/mm Time/s RMSE/mm Time/s RMSE/mm Time/s Armadillo 0.0288 3.21 0.0168 2.19 0.00730 0.437 Dragon 0.0363 3.77 0.0218 3.25 0.0125 0.528 表 3 真实室内场景物体点云配准定量分析结果
Table 3. Quantitative analysis results of object point cloud data registration in indoor scene
模型 源点云数/个 源点云特征点数/个 目标点云数/个 目标点云特征点数/个 RMSE/mm 平均误差/mm 耗时/s 平均耗时/s Chair 8549 3702 10431 4847 0.0686 0.544 Kettle 3713 1359 3879 1449 0.0633 0.0742 0.487 0.572 Mannequin 45292 16098 46507 16462 0.0907 0.686 -
[1] 杨鹏程, 杨朝, 孟杰, 等. 基于法向量和面状指数特征的文物点云棱界配准方法[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(3):654-662. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0156YANG P CH, YANG ZH, MENG J, et al. Aligning method for point cloud prism boundaries of cultural relics based on normal vector and faceted index features[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(3): 654-662. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0156 [2] ZOU ZH, LANG H, LOU Y X, et al. Plane-based global registration for pavement 3D reconstruction using hybrid solid-state LiDAR point cloud[J]. Automation in Construction, 2023, 152: 104907. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2023.104907 [3] CAO T, LIU Y P, DAI J J, et al. Local scanned point-cloud registration of aeroengine pipeline system based on axial constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2023, 72: 2527011. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2023.3256460 [4] DENG Y H, CHEN G H, LIU X L, et al. 3D pose recognition of small special-shaped sheet metal with multi-objective overlapping[J]. Electronics, 2023, 12(12): 2613. doi: 10.3390/electronics12122613 [5] SHI X Y, PENG J J, LI J P, et al. The iterative closest point registration algorithm based on the normal distribution transformation[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2019, 147: 181-190. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2019.01.219 [6] AIGER D, MITRA N J, COHEN-OR D. 4-points congruent sets for robust pairwise surface registration[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2008, 27(3): 1-10. [7] 傅瑶, 陈鹏, 郭贵松, 等. 基于4PCS和SICP的点云配准方法在钢轨磨耗计算中的应用[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报,2022,36(12):210-218. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.B2105036FU Y, CHEN P, GUO G S, et al. Application of the point cloud registration method based on 4PCS and SICP in rail wear calculation[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation, 2022, 36(12): 210-218. (in Chinese). doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.B2105036 [8] THEILER P W, WEGNER J D, SCHINDLER K. Keypoint-based 4-points congruent sets–automated marker-less registration of laser scans[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2014, 96: 149-163. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2014.06.015 [9] TAO W Y, LIU J B, XU D, et al. Automatic registration of point clouds by combining local shape descriptor and G4PCS algorithm[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2023, 16: 6339-6351. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2023.3293409 [10] BESL P J, MCKAY N D. Method for registration of 3-D shapes[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1992, 1611: 586-606. doi: 10.1117/12.57955 [11] 林森, 张强. 应用邻域点信息描述与匹配的点云配准[J]. 光学 精密工程,2022,30(8):984-997. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223008.0984LIN S, ZHANG Q. Point cloud registration using neighborhood point information description and matching[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(8): 984-997. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223008.0984 [12] YAO Z W, ZHAO Q X, LI X F, et al. Point cloud registration algorithm based on curvature feature similarity[J]. Measurement, 2021, 177: 109274. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109274 [13] LV CH L, LIN W S, ZHAO B Q. KSS-ICP: point cloud registration based on Kendall shape space[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2023, 32: 1681-1693. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2023.3251021 [14] LIU Y SH, CHEN X D, WANG K F, et al. A Chebyshev metamodel based BnB approach to efficiently search global optimum for 3D ICP point set registration[J]. Computer Aided Geometric Design, 2023, 101: 102178. doi: 10.1016/j.cagd.2023.102178 [15] XIE L F, ZHU Y Y, YIN M, et al. Self-feature-based point cloud registration method with a novel convolutional Siamese point net for optical measurement of blade profile[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2022, 178: 109243. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2022.109243 [16] ZHANG ZH Y, SUN J D, DAI Y CH, et al. Self-supervised rigid transformation equivariance for accurate 3D point cloud registration[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2022, 130: 108784. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2022.108784 [17] 何宽, 孙瑞, 官云兰, 等. 基于逐点前进法的点云数据精简[J]. 测绘通报,2022(9):167-169.HE K, SUN R, GUAN Y L, et al. Point cloud data simplification based on point-by-point advancing method[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2022(9): 167-169. (in Chinese). [18] 李茂月, 赵伟翔, 马康盛, 等. 结构光检测点云精简与重构参数自动调节方法[J]. 仪器仪表学报,2022,43(8):122-130.LI M Y, ZHAO W X, MA K SH, et al. Point cloud simplification and reconstruction parameters’ automatic adjustment method of structured light detection[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2022, 43(8): 122-130. (in Chinese). [19] FITZGIBBON A W. Robust registration of 2D and 3D point sets[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2003, 21(13-14): 1145-1153. doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2003.09.004 [20] 王宾, 刘林, 侯榆青, 等. 应用改进迭代最近点方法的三维心脏点云配准[J]. 光学 精密工程,2020,28(2):474-484.WANG B, LIU L, HOU Y Q, et al. Three-dimensional cardiac point cloud registration by improved iterative closest point method[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(2): 474-484. (in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: