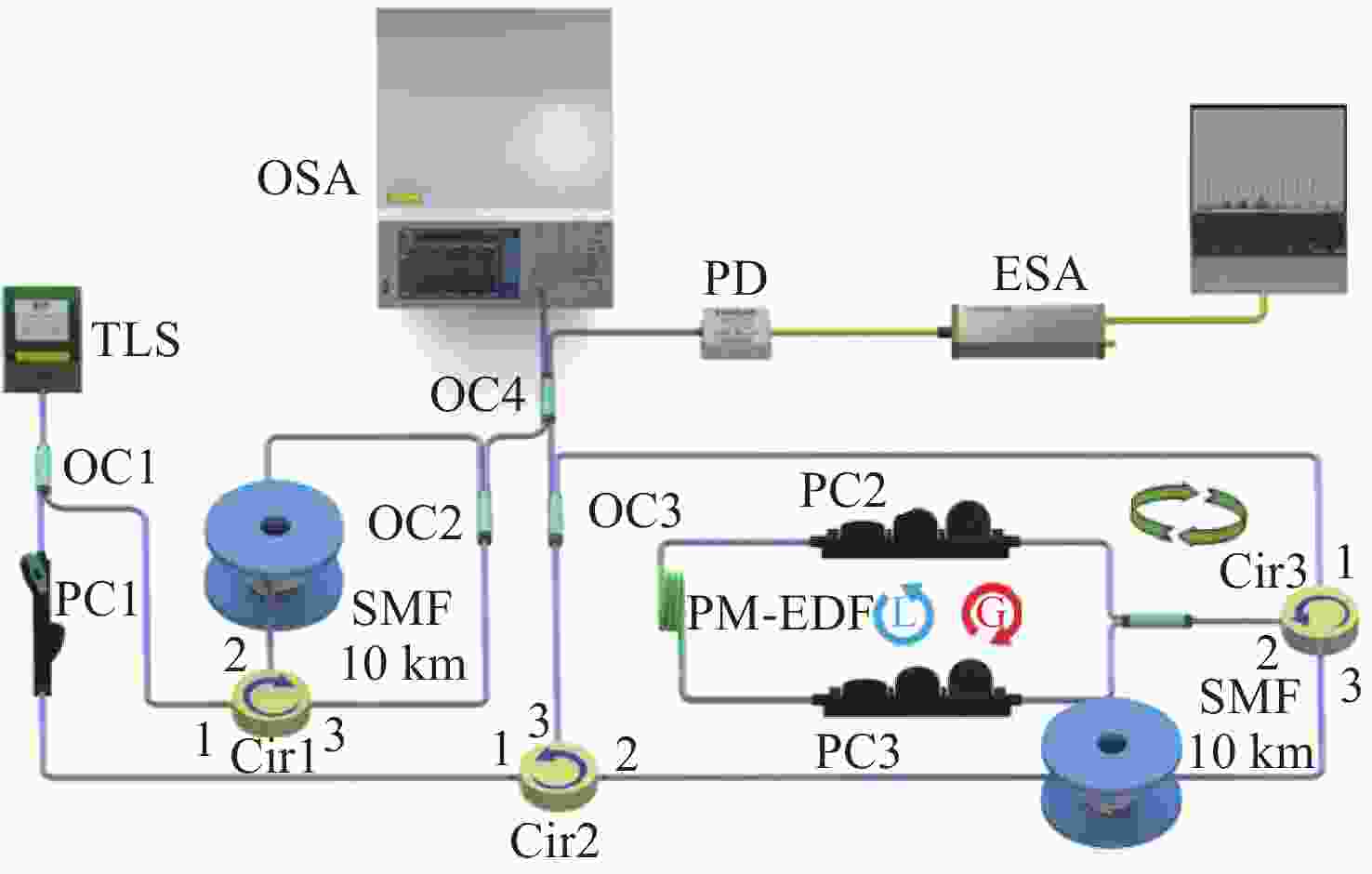
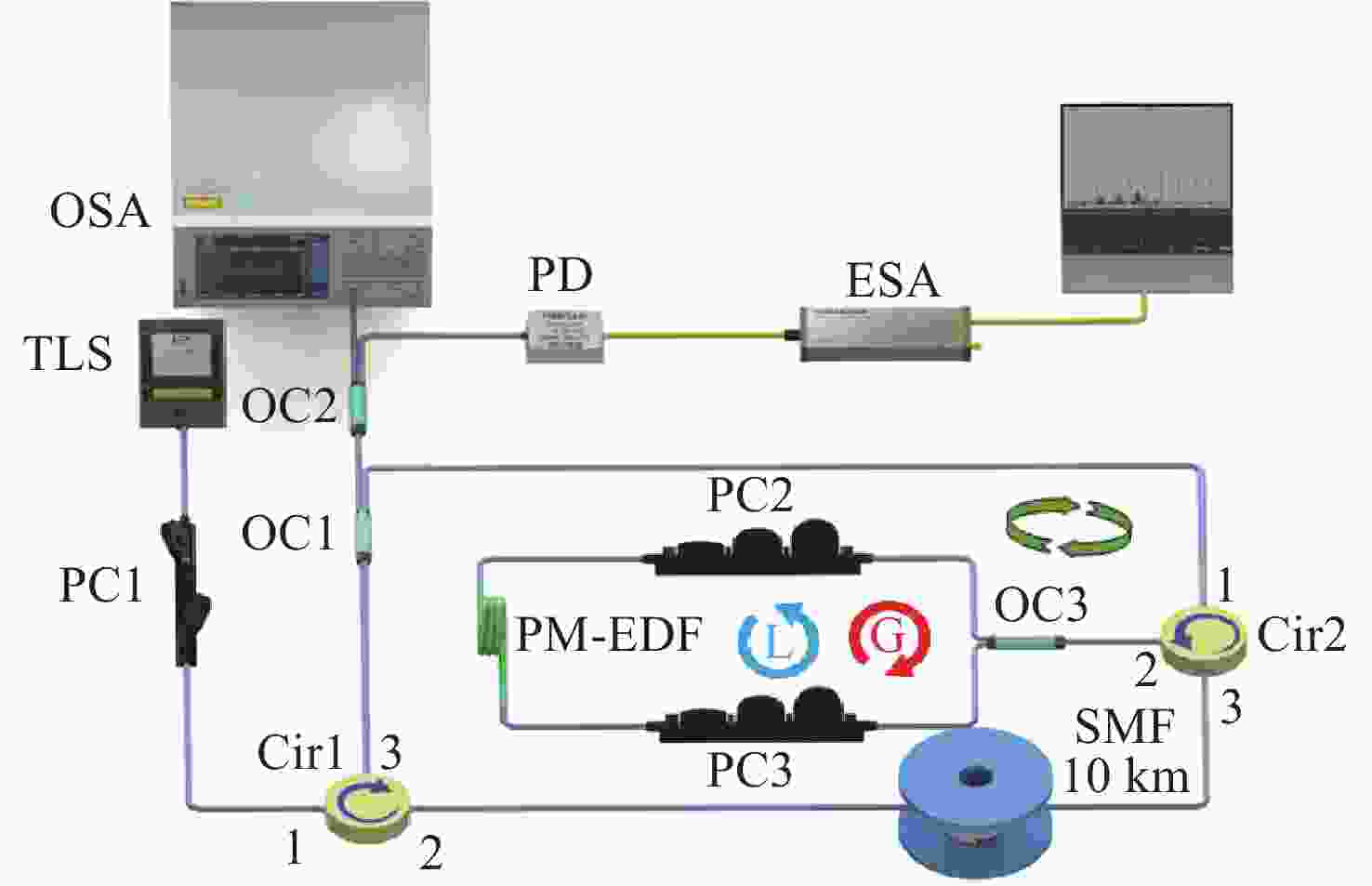
Widely-wavelength-tunable brillouin fiber laser with improved optical signal-to-noise ratio based on parity-time symmetric and saturable absorption effect
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2024-0016
-
摘要:
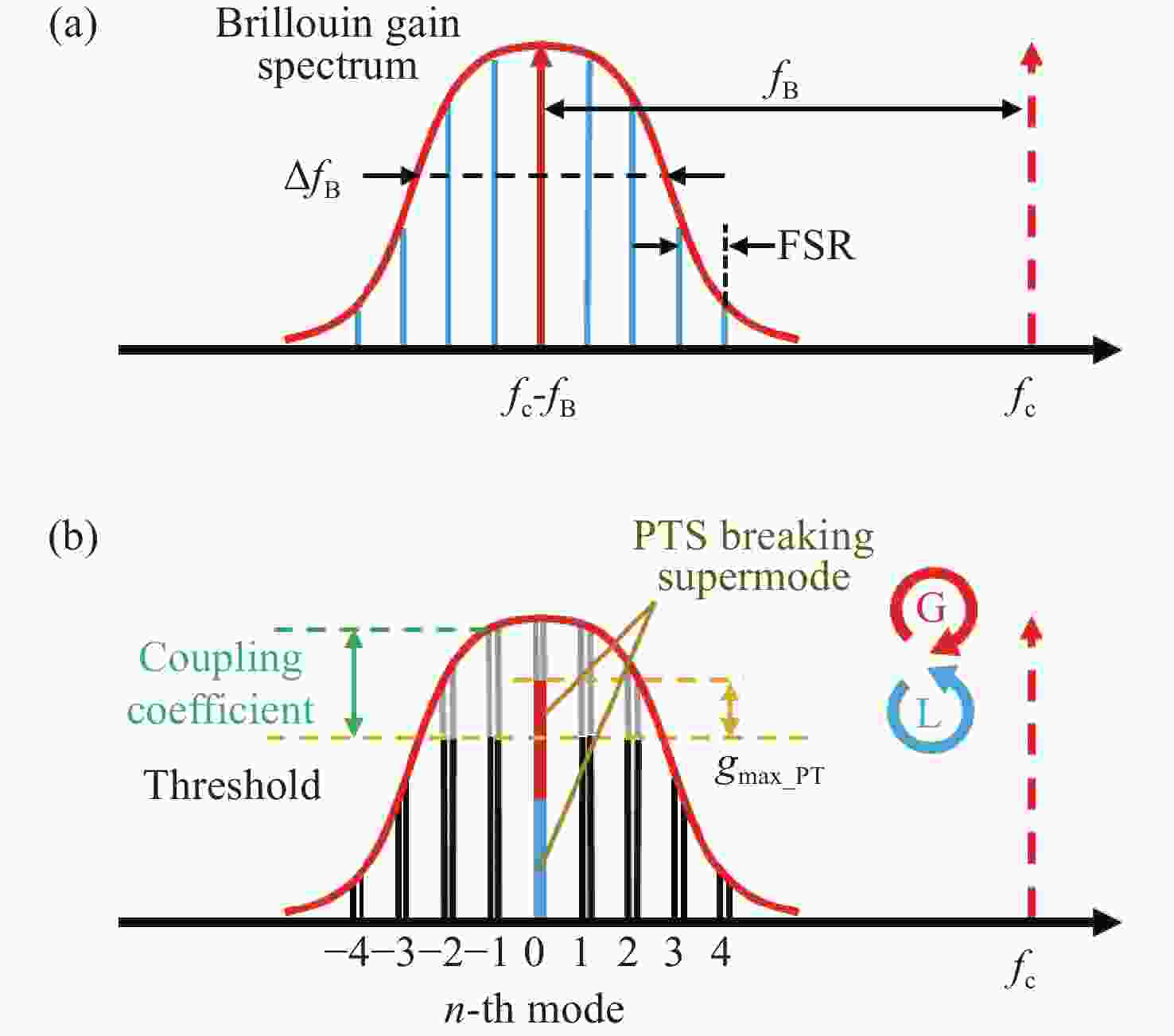
本文提出了一种基于宇称时间对称与饱和吸收效应的宽可调谐高光信噪比布里渊光纤金宝搏188软件怎么用 器。这种新型布里渊光纤金宝搏188软件怎么用 器是通过使用保偏掺铒光纤Sagnac环实现宇称时间对称和饱和吸收效应的。保偏掺铒光纤Sagnac环是由一个保偏掺铒光纤、一个耦合器和两个偏振控制器构成的。利用保偏掺铒光纤固有的双折射特性,在注入Stokes信号时形成两个处于正交偏振态的反馈环。其中一个环路在Sagnac环内提供顺时针方向的增益,而另一个环路在逆时针方向产生损耗。当饱和吸收效应参与的受激布里渊散射增益和损耗相平衡,并且增益值大于耦合系数时,由于宇称时间对称性被破坏,通过调整偏振控制器改变保偏掺铒光纤的偏振态,可获得单纵模布里渊光纤金宝搏188软件怎么用 器。与以往的布里渊光纤金宝搏188软件怎么用 器相比,本文提出的金宝搏188软件怎么用 器具有更精简的结构和更宽的波长可调范围,且不受掺铒光纤放大器带宽的限制,同时仍保持窄线宽单纵模输出。此外,由于保偏掺铒光纤的饱和吸收效应,提高了宇称时间对称受激布里渊散射增益对比度,因此获得了更高的光信噪比。实验结果表明,该金宝搏188软件怎么用 器具有
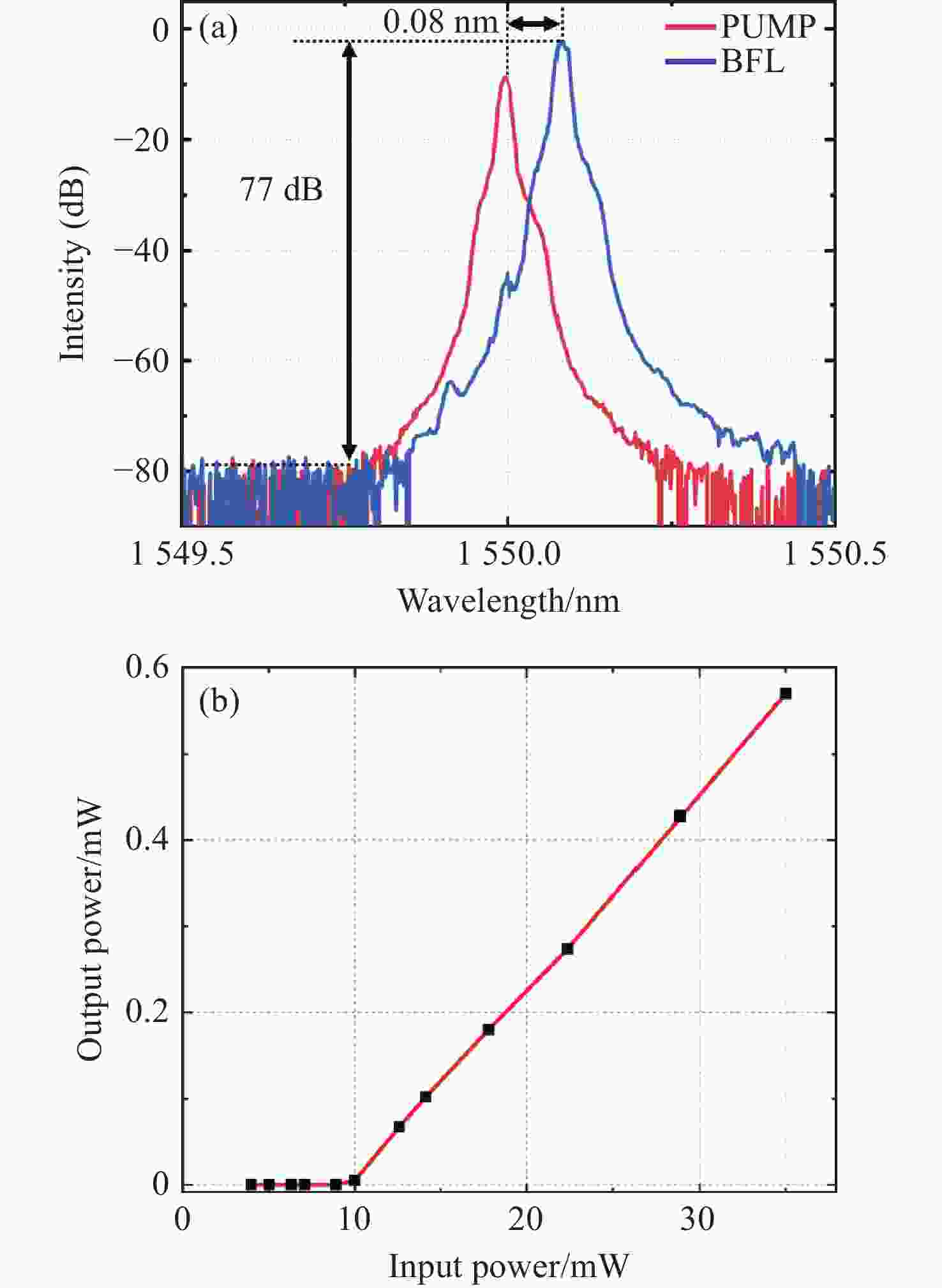
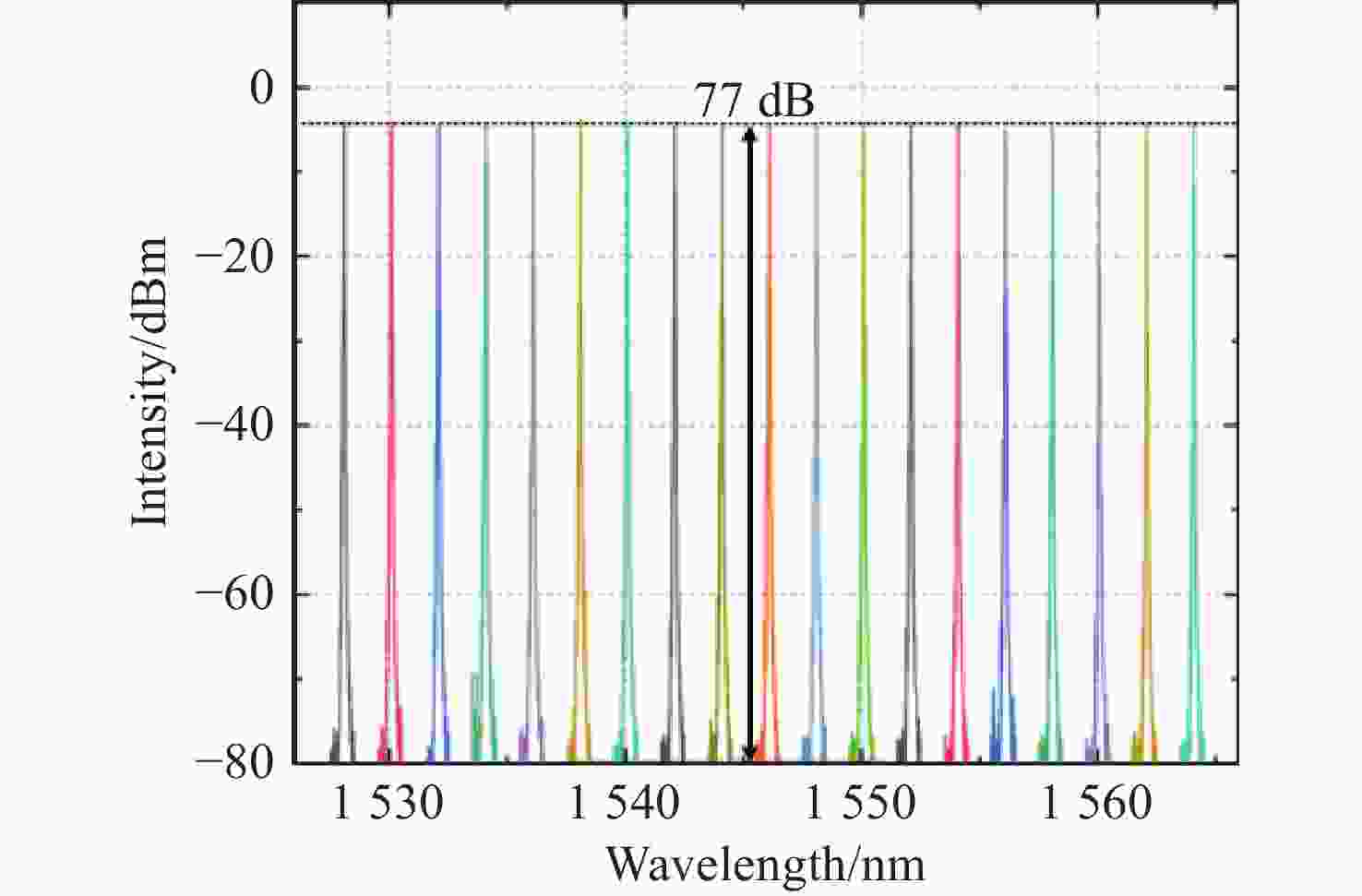
1526.088 ~1565.498 nm宽可调范围、77 dB光信噪比和140.5 Hz线宽。-
关键词:
- 布里渊光纤金宝搏188软件怎么用 器 /
- 波长可调 /
- 宇称时间对称 /
- 高光信噪比 /
- 窄线宽
Abstract:A widely-wavelength-tunable Brillouin fiber laser (BFL) with improved optical signal-to-noise ratio (OSNR) based on parity-time (PT) symmetric and saturable absorption (SA) effect is present. This novel BFL realizes PT symmetry and SA effect through polarization-maintaining erbium-doped fiber (PM-EDF) Sagnac loop, which is composed of a PM-EDF, a coupler and two polarization controllers (PCs). By using the inherent birefringence characteristic of PM-EDF, two feedback loops in orthogonal polarization state are formed when the Strokes signal in injected. One of these loops provides gain in the clockwise direction with in the Sagnac loop, while the other loop generates loss in the counterclockwise direction. By adjusting the PCs to control the polarization state of the PM-EDF, a single-longitudinal-mode (SLM) BFL can be achieved, as the PT symmetry is broken when the SA participating stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) gain and loss are well-matched and the gain surpasses the coupling coefficient. Compared to previous BFLs, the proposed BFL has a more streamlined structure and a wider wavelength tunable range, at the same time, it is not being limited by the bandwidth of the erbium-doped fiber amplifier while still maintaining narrow linewidth SLM output. Additionally, thanks to SA effect of the PM-EDF, the PT symmetric SBS gain contract is enhanced, resulting in a higher optical signal-to-noise (OSNR). The experimental results show that the laser has a wide tunable range of
1526.088 nm to1565.498 nm, an improved OSNR of 77 dB, and a fine linewidth as small as 140.5 Hz.-
Key words:
- Brillouin fiber laser /
- widely-wavelength-tunable /
- parity-time symmetric /
- high OSNR /
- narrow linewidth
-
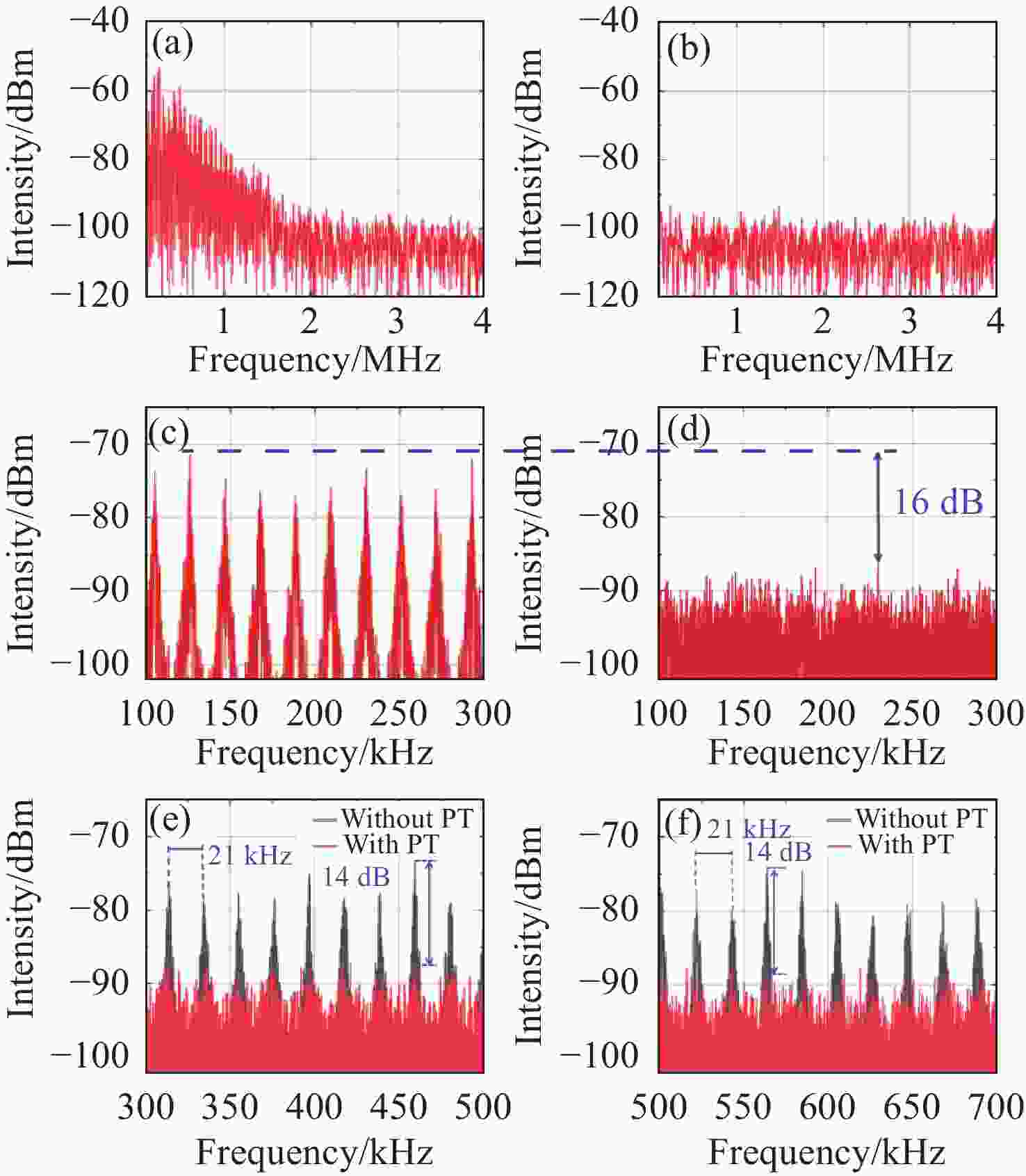
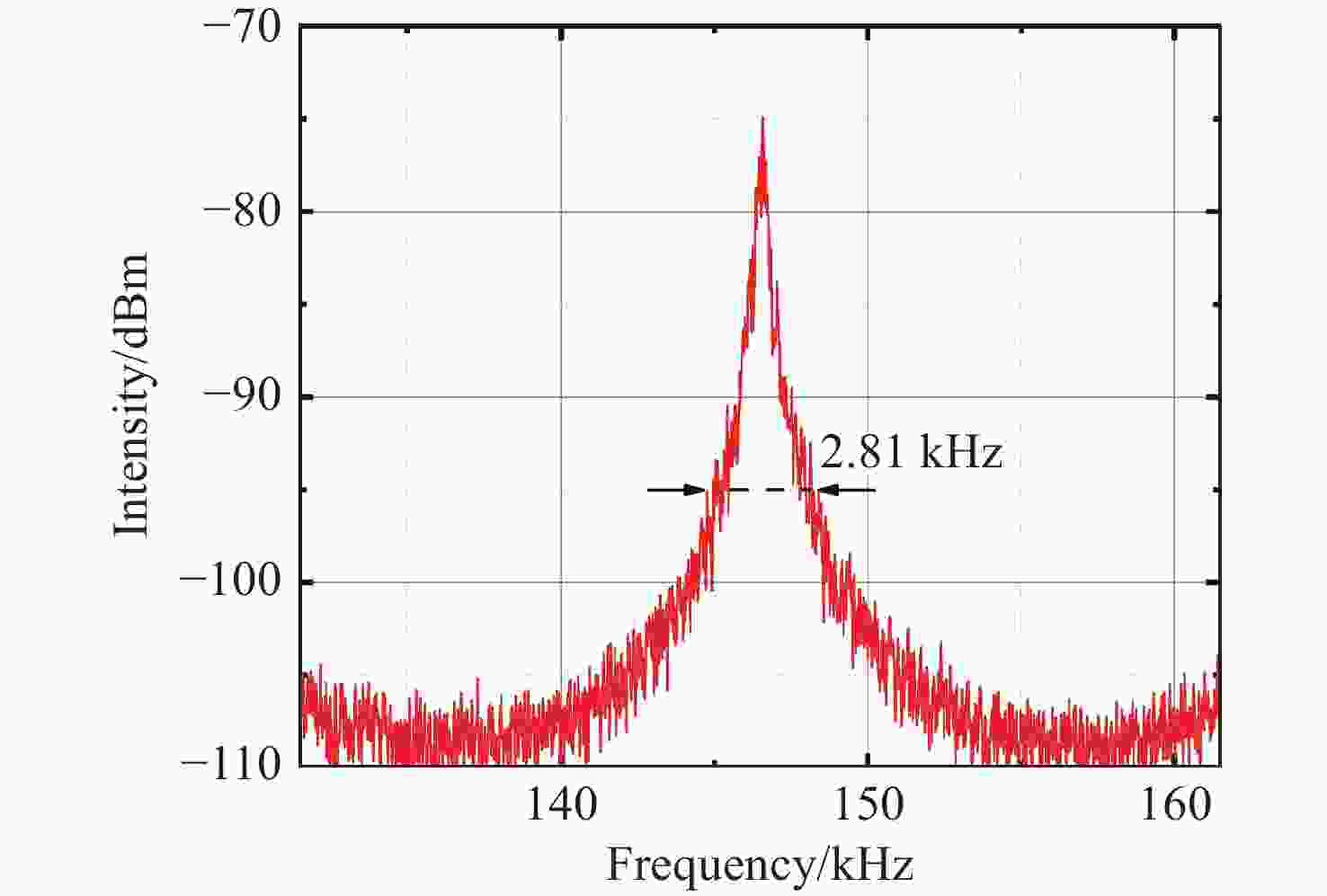
Figure 5. The spectral analysis results of the frequency beat signals emitted from the PD. (a) Unbroken PT-symmetry and (b) broken PT-symmetry with their magnified view under 0−4 MHz frequency range; (c) and (d) are enlarged views at 100−300 kHz respectively; (e) and (f) present a comparative diagram of the measured spectra, demonstrating the effects of PT-symmetry under 300−500 kHz and 500−700 kHz frequency ranges respectively
-
[1] BRILLOUIN L. Diffusion de la lumière et des rayons X par un corps transparent homogène[J]. Annales de Physique, 1922, 9(17): 88-122. doi: 10.1051/anphys/192209170088 [2] MANDELSTAM L I. Light scattering by inhomogeneous media[J]. Zh Russ Fiz-Khim Ova, 1926, 58: 381-391. [3] GARMIRE E. Perspectives on stimulated Brillouin scattering[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2017, 19(1): 011003. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/aa5447 [4] AL-MASHHADANI M K S, AL-MASHHADANI T F, GOKTAS H H. Broadly tunable 40 GHz Brillouin frequency spacing multiwavelength Brillouin–Erbium fiber laser for DWDM[J]. Optics Communications, 2019, 451: 116-123. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2019.06.040 [5] AL-MANSOORI M H, AL-SHERIYANI A, YOUNIS M A A, et al. Widely tunable multiwavelength Brillouin-erbium fiber laser with triple Brillouin-shift wavelength spacing[J]. Optical Fiber Technology, 2018, 41: 21-26. doi: 10.1016/j.yofte.2017.12.012 [6] WANG L Y, LIU Y, YOU Y J, et al. Microwave photonic filter with a sub-kHz bandwidth based on a double ring Brillouin fiber laser[J]. Optics Letters, 2022, 47(16): 4143-4146. doi: 10.1364/OL.469193 [7] BASTIANINI F, DI SANTE R, FALCETELLI F, et al. Optical fiber sensing cables for Brillouin-based distributed measurements[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(23): 5172. doi: 10.3390/s19235172 [8] XU Y P, LU P, BAO X Y. Compact single-end pumped Brillouin random fiber laser with enhanced distributed feedback[J]. Optics Letters, 2020, 45(15): 4236-4239. doi: 10.1364/OL.398593 [9] LIU Y, SHANG Y, YI X G, et al. Triple Brillouin frequency spacing Brillouin fiber laser sensor for temperature measurement[J]. Optical Fiber Technology, 2020, 54: 102106. doi: 10.1016/j.yofte.2019.102106 [10] SHANG Y, GUO R R, LIU Y, et al. Managing Brillouin frequency spacing for temperature measurement with Brillouin fiber laser sensor[J]. Optical and Quantum Electronics, 2020, 52(4): 211. doi: 10.1007/s11082-020-02330-8 [11] ZHU K Y, HE J Y, CHANG K, et al. The multi-wavelength Brillouin laser based on highly nonlinear fiber[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2022, 12169: 1216935. doi: 10.1117/12.2623571 [12] LOH W, YEGNANARAYANAN S, O’DONNELL F, et al. Ultra-narrow linewidth Brillouin laser with nanokelvin temperature self-referencing[J]. Optica, 2019, 6(2): 152-159. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.6.000152 [13] AHMAD H, RAZAK N F, ZULKIFLI M Z, et al. Ultra-narrow linewidth single longitudinal mode Brillouin fiber ring laser using highly nonlinear fiber[J]. Laser Physics Letters, 2013, 10(10): 105105. doi: 10.1088/1612-2011/10/10/105105 [14] PARVIZI R, AROF H, ALI N M, et al. 0.16 nm spaced multi-wavelength Brillouin fiber laser in a figure-of-eight configuration[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2011, 43(4): 866-869. [15] OU ZH H, BAO X Y, LI Y, et al. Ultranarrow linewidth Brillouin fiber laser[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2014, 26(20): 2058-2061. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2014.2346783 [16] BENDER C M, BOETTCHER S. Real spectra in non-Hermitian Hamiltonians having P T symmetry[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1998, 80(24): 5243-5246. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.80.5243 [17] ÖZDEMIR Ş K, ROTTER S, NORI F, et al. Parity–time symmetry and exceptional points in photonics[J]. Nature Materials, 2019, 18(8): 783-798. doi: 10.1038/s41563-019-0304-9 [18] EL-GANAINY R, MAKRIS K G, KHAJAVIKHAN M, et al. Non-Hermitian physics and PT symmetry[J]. Nature Physics, 2018, 14(1): 11-19. doi: 10.1038/nphys4323 [19] LI P, DAI ZH, FAN ZH Q, et al. Parity–time-symmetric frequency-tunable optoelectronic oscillator with a single dual-polarization optical loop[J]. Optics Letters, 2020, 45(11): 3139-3142. doi: 10.1364/OL.394719 [20] ZHANG J J, LI L ZH, WANG G Y, et al. Parity-time symmetry in wavelength space within a single spatial resonator[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 3217. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16705-8 [21] ZHANG J J, YAO J P. Parity-time–symmetric optoelectronic oscillator[J]. Science Advances, 2018, 4(6): eaar6782. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aar6782 [22] LI L ZH, CAO Y, ZHI Y Y, et al. Polarimetric parity-time symmetry in a photonic system[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2020, 9: 169. [23] ZHU Y Y, ZHAO Y S, FAN J H, et al. Modal gain analysis of parity-time-symmetric distributed feedback lasers[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2016, 22(5): 1500207. [24] DAI ZH, FAN ZH Q, LI P, et al. Widely wavelength-tunable parity-time symmetric single-longitudinal-mode fiber ring laser with a single physical loop[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2021, 39(7): 2151-2157. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2020.3044067 [25] LIU Y, WANG L Y, XU X, et al. Narrow linewidth parity-time symmetric Brillouin fiber laser based on a dual-polarization cavity with a single micro-ring resonator[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(25): 44545-44555. doi: 10.1364/OE.475957 [26] LIU Y, WANG L Y, YOU Y J, et al. Single longitudinal mode parity-time symmetric Brillouin fiber laser based on lithium niobate phase modulator sagnac loop[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2023, 41(5): 1552-1558. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2022.3224208 [27] LIU Y, GUO R R, ZHAO J J, et al. An EDFA-gain equalizer based on a Sagnac loop with an unpumped erbium-doped fiber[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2021, 39(13): 4496-4502. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2021.3071422 [28] MAKRIS K G, EL-GANAINY R, CHRISTODOULIDES D N, et al. Beam dynamics in P T symmetric optical lattices[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2008, 100(10): 103904. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.103904 [29] DEBUT A, RANDOUX S, ZEMMOURI J. Linewidth narrowing in Brillouin lasers: theoretical analysis[J]. Physical Review A, 2000, 62(2): 023803. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.62.023803 [30] POLLNAU M, EICHHORN M. Spectral coherence, Part I: passive-resonator linewidth, fundamental laser linewidth, and Schawlow-Townes approximation[J]. Progress in Quantum Electronics, 2020, 72: 100255. doi: 10.1016/j.pquantelec.2020.100255 [31] WANG G M, ZHAN L, LIU J M, et al. Watt-level ultrahigh-optical signal-to-noise ratio single-longitudinal-mode tunable Brillouin fiber laser[J]. Optics Letters, 2013, 38(1): 19-21. doi: 10.1364/OL.38.000019 -





 下载:
下载: