On-line detection of soluble solids content of apples from different origins by visible and near-infrared spectroscopy
-
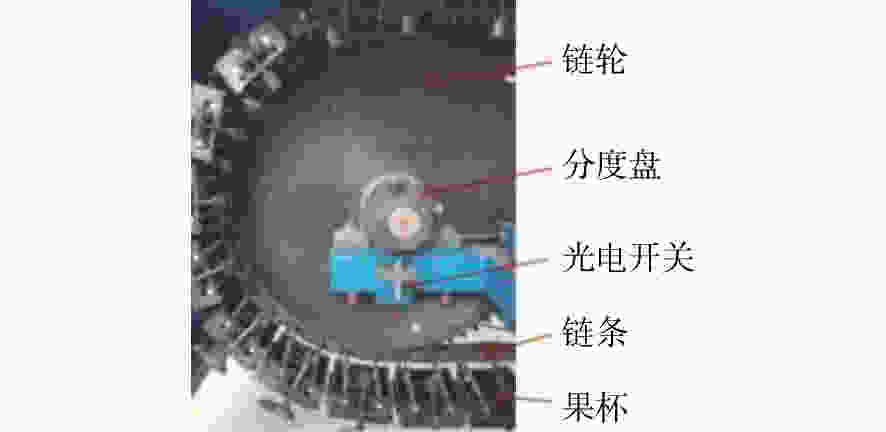
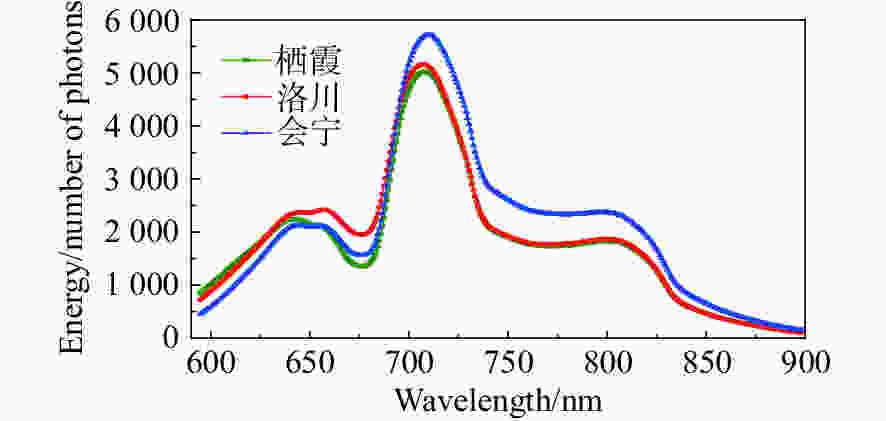
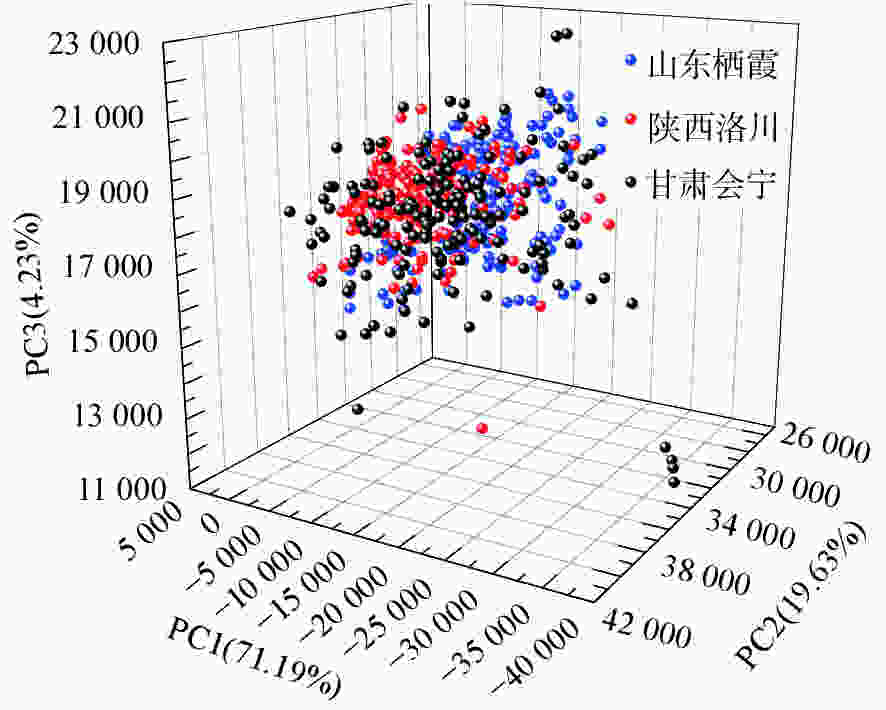
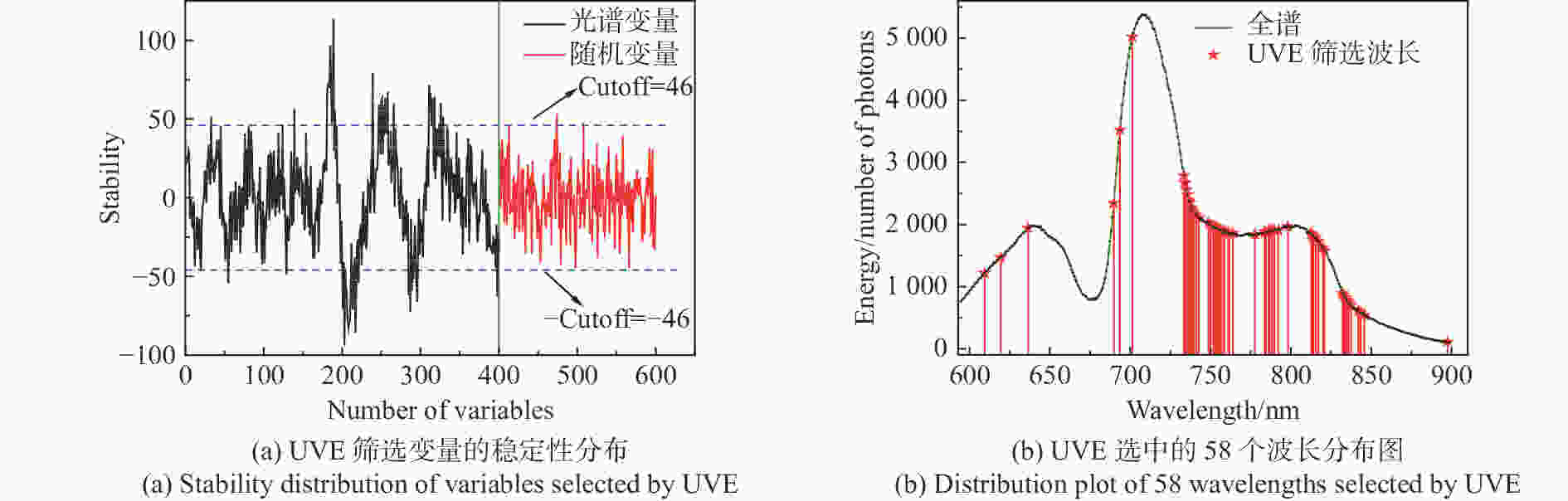
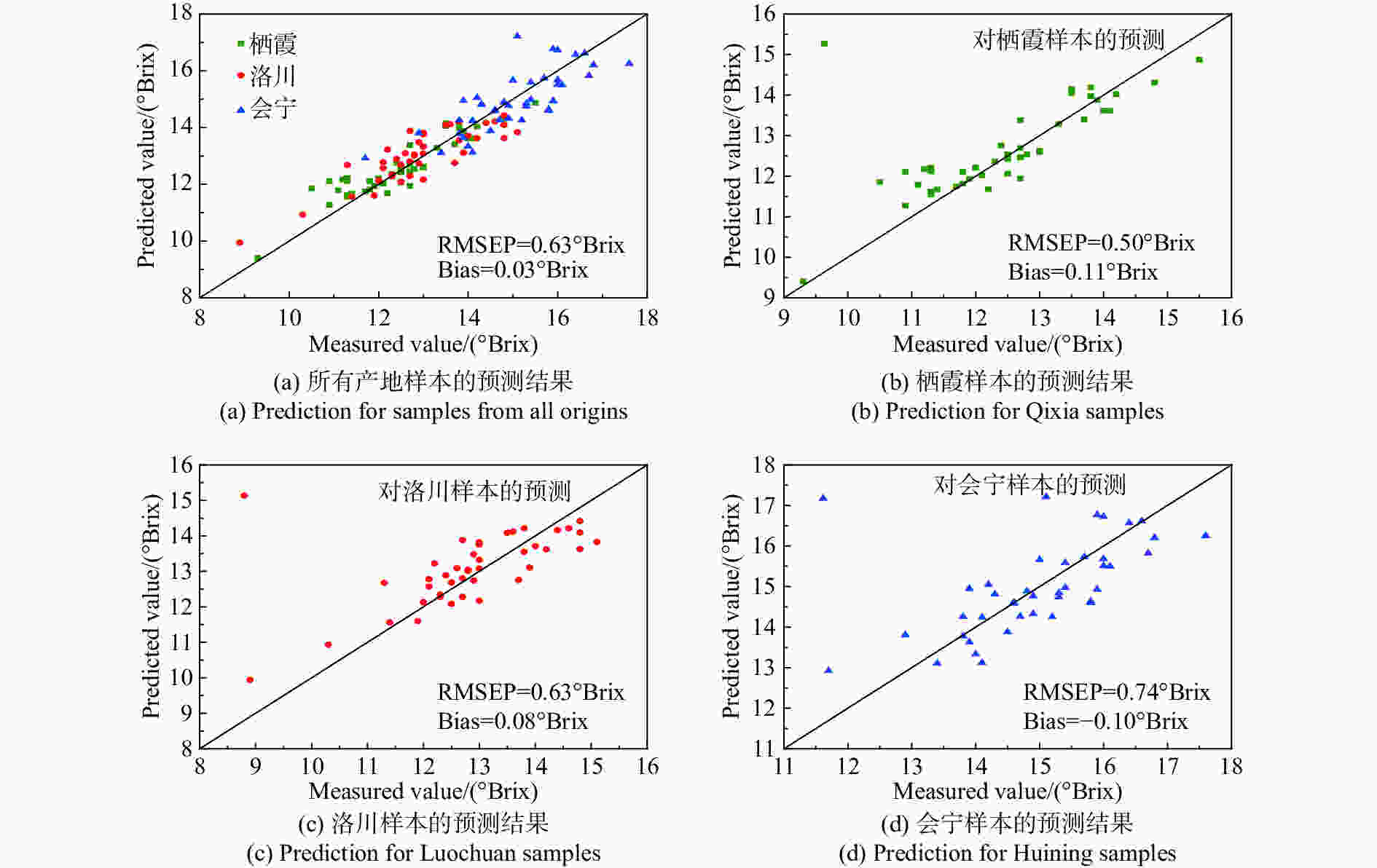
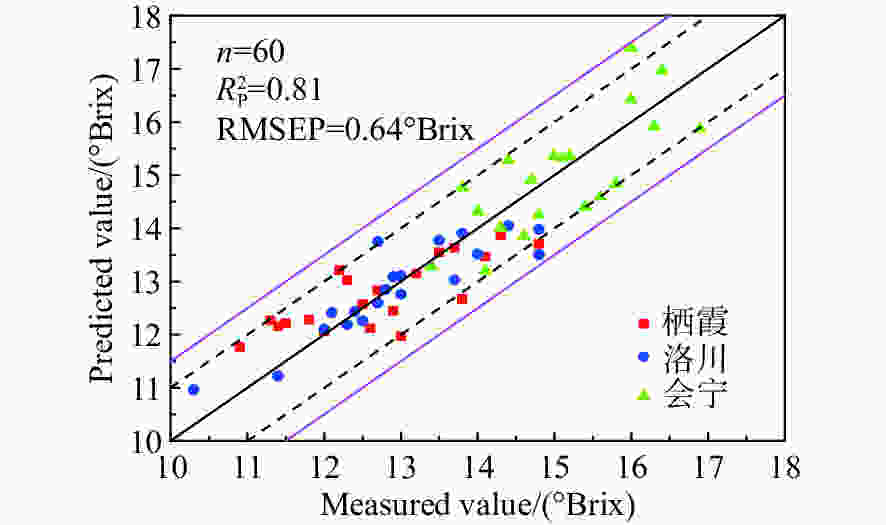
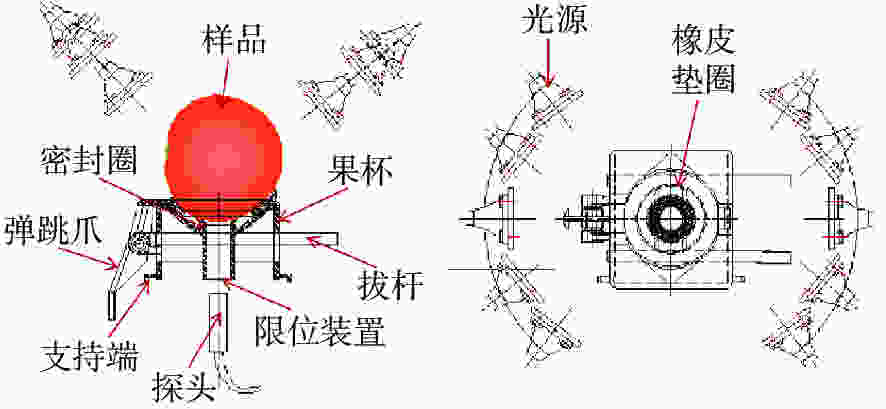
摘要: 为了实现不同产地苹果糖度的快速在线无损检测,减少产地差异对近红外光谱检测模型的影响,建立了不同产地苹果糖度的在线检测通用模型。首先,采用水果动态在线检测设备采集了包括栖霞、洛川与会宁3个产地的红富士苹果的漫透射光谱。其次,采用偏最小二乘算法(PLS),结合无信息变量消除(UVE)方法,筛选出58个特征变量,建立了苹果糖度的UVE-PLS通用模型,该模型对个体产地预测集及总预测集的均方根误差分别为0.50~0.74°Brix与0.63°Brix,较原始个体模型分别提高了23.2%~44.4%与35.7%。最后,提出了一个新的外部验证样本集对模型性能进行评价,其残留预测偏差为2.33,预测值在±1.0°Brix和±1.5°Brix误差范围内的占比分别为85%与100%。实验结果表明:建立多个产地苹果糖度的在线检测通用模型,能够提高其他产地样本糖度的预测稳健性,并且采用合适的波长筛选方法能够简化模型。开发不同产地水果内部品质通用模型在波长有限的光谱设备中具有良好的应用潜力。Abstract: In order to realize fast, on-line, non-destructive testing of the Soluble Solids Content (SSC) of apples from different origins, and to reduce the effect of origin variability on NIR models, a universal model for predicting the SSC of apples from different origins is established. Firstly, the diffuse transmission spectra of Fuji apples from Qixia, Luochuan and Huining are collected with fruit dynamic online detection equipment. Then, 58 characteristic variables are selected and a UVE-PLS universal model for predicting the SSC of apples is established using the Partial Least Squares (PLS) algorithm combined with Uninformative Variable Elimination (UVE). The root mean square errors of single-origin prediction sets and the total-origin prediction set are 0.50~0.74° Brix and 0.63° Brix, respectively, which increase by 23.2%~44.4% and 35.7% respectively compared to the original individual model. Finally, a new external sample set is used to assess the performance of the model, showing a residual prediction deviation of 2.33 and ratios of the predicted values within the error range of ±1.0° Brix and ±1.5° Brix of 85% and 100%, respectively. Experimental results indicate that the establishment of a universal model for on-line detection of the SSC of apples, including those from multiple origins can improve the robustness of predicting the SSC of the samples from other origins. The results also show that an appropriate wavelength screening method can simplify the model. The development of a common model for the internal quality of fruit from different origins has strong potential for applications in wavelength-limited spectroscopy equipment.
-
Key words:
- online detection /
- near infrared spectroscopy /
- soluble solids /
- partial least squares
-
表 1 样本集糖度含量统计
Table 1. Statistical values of the SSC(°Brix)for sample sets
产地 校正集 预测集 数量 范围 平均值 标准差 数量 范围 平均值 标准差 1 129 8.8~16.6 12.93 1.43 43 9.3~15.5 12.47 1.24 2 135 8.5~16.4 13 1.28 41 8.9~15.1 12.93 1.23 3 127 10.1~18.2 14.97 1.21 40 11.7~17.6 15.03 1.17 总 391 8.5~18.2 13.62 1.61 124 8.9~17.6 13.45 1.64 表 2 单个产地的PLS建模结果
Table 2. Results of PLS modeling for single origin
产地 LVs 校正集 预测集 RPD $R_{\rm{C}}^2$ RMSEC(°Brix) $R_{\rm{P}}^2 $ RMSEP(°Brix) 1 9 0.92 0.40 0.90 0.41 3.02 2 10 0.89 0.42 0.85 0.47 2.62 3 11 0.86 0.46 0.80 0.51 2.29 表 3 不同产地红富士苹果的预测结果
Table 3. Prediction results of Fuji apples from different origins
产地 预测集 1 2 3 总 $R_{\rm{P}}^2 $ RMSEP(°Brix) $R_{\rm{P}}^2 $ RMSEP(°Brix) $R_{\rm{P}}^2 $ RMSEP(°Brix) $R_{\rm{P}}^2 $ RMSEP(°Brix) 1 / / 0.54 0.82 0.73 1.24 0.42 1.30 2 0.54 0.90 / / 0.67 1.34 0.67 0.98 3 0.73 1.44 0.72 1.25 / / 0.68 1.27 表 4 苹果糖度通用模型预测结果
Table 4. Results of SSC of apples predicted by universal modeling
模型 变量数 LVs $R_{\rm{C}}^2 $ RMSEC(°Brix) $R_{\rm{P}}^2 $ RMSEP(°Brix) RPD Ori-PLS 400 12 0.84 0.64 0.85 0.63 2.60 UVE-PLS 58 8 0.82 0.68 0.85 0.63 2.60 表 5 UVE-PLS糖度通用模型的实际性能
Table 5. The practical performance of UVE-PLS universal model for SSC
RMSEP/(°Brix) RPD 栖霞 洛川 会宁 总 总 0.67 0.51 0.72 0.64 2.33 -
[1] GIOVANELLI G, SINELLI N, BEGHI R, et al. NIR spectroscopy for the optimization of postharvest apple management[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 2014, 87: 13-20. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2013.07.041 [2] FAN SH X, ZHANG B H, LI J B, et al. Effect of spectrum measurement position variation on the robustness of NIR spectroscopy models for soluble solids content of apple[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2016, 143: 9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2015.12.012 [3] MENDOZA F, LU R F, ARIANA D, et al. Integrated spectral and image analysis of hyperspectral scattering data for prediction of apple fruit firmness and soluble solids content[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 2011, 62(2): 149-160. [4] 高升, 王巧华, 李庆旭, 等. 基于近红外光谱的红提维生素C含量、糖度及总酸含量无损检测方法[J]. 分析化学,2019,47(6):941-949.GAO SH, WANG Q H, LI Q X, et al. Non-destructive detection of vitamin c, sugar content and total acidity of red globe grape based on near-infrared spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 47(6): 941-949. (in Chinese) [5] 史云颖, 李敬岩, 褚小立. 多元校正模型传递方法的进展与应用[J]. 分析化学,2019,47(4):479-487.SHI Y Y, LI J Y, CHU X L. Progress and applications of multivariate calibration model transfer methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 47(4): 479-487. (in Chinese) [6] 王凡, 李永玉, 彭彦昆, 等. 基于可见/近红外透射光谱的番茄红素含量无损检测方法研究[J]. 分析化学,2018,46(9):1424-1431.WANG F, LI Y Y, PENG Y K, et al. Nondestructive determination of lycopene content based on visible/near infrared transmission spectrum[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 46(9): 1424-1431. (in Chinese) [7] 路皓翔, 徐明昌, 张卫东, 等. 基于压缩自编码融合极限学习机的柑橘黄龙病鉴别方法[J]. 分析化学,2019,47(5):652-660.LU H X, XU M CH, ZHANG W D, et al. Identification of citrus huanglongbing based on contractive auto-encoder combined extreme learning manchine[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 47(5): 652-660. (in Chinese) [8] 郭文川, 王铭海, 谷静思, 等. 近红外光谱结合极限学习机识别贮藏期的损伤猕猴桃[J]. 光学 精密工程,2013,21(10):2720-2727. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20132110.2720GUO W CH, WANG M H, GU J S, et al. Identification of bruised kiwifruits during storage by near infrared spectroscopy and extreme learning machine[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2013, 21(10): 2720-2727. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20132110.2720 [9] 郭志明, 黄文倩, 彭彦昆, 等. 自适应蚁群优化算法的近红外光谱特征波长选择方法[J]. 分析化学,2014,42(4):513-518.GUO ZH M, HUANG W Q, PENG Y K, et al. Adaptive ant colony optimization approach to characteristic wavelength selection of NIR spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 42(4): 513-518. (in Chinese) [10] ZHANG B H, HUANG W Q, GONG L, et al. Computer vision detection of defective apples using automatic lightness correction and weighted RVM classifier[J]. Journal of Food Engineering, 2015, 146: 143-151. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2014.08.024 [11] ZHANG B H, DAI D J, HUANG J CH, et al. Influence of physical and biological variability and solution methods in fruit and vegetable quality nondestructive inspection by using imaging and near-infrared spectroscopy techniques: a review[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2018, 58(12): 2099-2118. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2017.1300789 [12] 樊书祥, 黄文倩, 郭志明, 等. 苹果产地差异对可溶性固形物近红外光谱检测模型影响的研究[J]. 分析化学,2015,43(2):239-244.FAN SH X, HUANG W Q, GUO ZH M, et al. Assessment of influence of origin variability on robustness of near infrared models for soluble solid content of apples[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 43(2): 239-244. (in Chinese) [13] LI X N, HUANG J CH, XIONG Y J, et al. Determination of soluble solid content in multi-origin ‘Fuji’ apples by using FT-NIR spectroscopy and an origin discriminant strategy[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2018, 155: 23-31. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2018.10.003 [14] JANNOK P, KAMITANI Y, HIRONAKA K, et al. Development of a near infrared calibration model with temperature compensation using common temperature-difference spectra for determining the Brix value of intact fruits[J]. Journal of Near Infrared Spectroscopy, 2017, 25(1): 26-35. doi: 10.1177/0967033516678516 [15] 王拓, 戴连奎, 马万武. 拉曼光谱结合后向间隔偏最小二乘法用于调和汽油辛烷值定量分析[J]. 分析化学,2018,46(4):623-629.WANG T, DAI L K, MA W W. Quantitative analysis of blended gasoline octane number using raman spectroscopy with backward interval partial least squares method[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 46(4): 623-629. (in Chinese) [16] 刘翠玲, 吴静珠, 孙晓荣. 近红外光谱技术在食品品质检测方法中的研究[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2016.LIU C L, WU J ZH, SUN X R. Study on Near Infrared Spectroscopy in Food Quality Testing Methods[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2016. (in Chinese) [17] CHANG CH W, LAIRD D A, MAUSBACH M J, et al. Near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy-principal components regression analyses of soil properties[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2001, 65(2): 480-490. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2001.652480x [18] ZHANG D Y, XU L, WANG Q Y, et al. The optimal local model selection for robust and fast evaluation of soluble solid content in melon with thick peel and large size by Vis-NIR spectroscopy[J]. Food Analytical Methods, 2019, 12(1): 136-147. doi: 10.1007/s12161-018-1346-3 [19] YUAN L M, CAI J R, SUN L, et al. Nondestructive measurement of soluble solids content in apples by a portable fruit analyzer[J]. Food Analytical Methods, 2016, 9(3): 785-794. doi: 10.1007/s12161-015-0251-2 [20] YUN Y H, LI H D, DENG B CH, et al. An overview of variable selection methods in multivariate analysis of near-infrared spectra[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 113: 102-115. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2019.01.018 -





 下载:
下载: