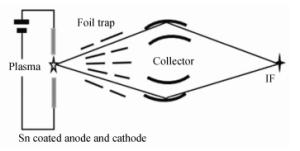
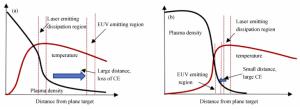
Research progress on laser-produced plasma light source for 13.5 nm extreme ultraviolet lithography
-
摘要: 半导体产业是高科技、信息化时代的支柱。光刻技术,作为半导体产业的核心技术之一,已成为世界各国科研人员的重点研究对象。本文综述了金宝搏188软件怎么用 等离子体13.5 nm极紫外光刻的原理和国内外研究发展概况,重点介绍了其金宝搏188软件怎么用 源、辐射靶材和多层膜反射镜等关键系统组成部分。同时,指出了在提高金宝搏188软件怎么用 等离子体13.5 nm极紫外光源输出功率的研究进程中所存在的主要问题,包括提高转换效率和减少光源碎屑。特别分析了目前已实现百瓦级输出的日本Gigaphoton公司和荷兰的ASML公司的极紫外光源装置。最后对该项技术的发展前景进行了总结与展望。
-
关键词:
- 13.5 nm极紫外光刻技术 /
- 金宝搏188软件怎么用 等离子体 /
- 极紫外光源 /
- 转换效率 /
- 光源碎屑 /
- 预脉冲金宝搏188软件怎么用
Abstract: The semiconductor industry is the backbone of the high-tech and information age. Lithography technology, one of the core technology of the semiconductor industry, has become a key research subject all around the world. This article mainly discusses the light source of 13.5 nm Extreme Ultraviolet Lithography (EUVL) by using Laser-Produced Plasma (LPP). It makes a brief introduction to the principles behind this technology and the development history of this field at home and abroad. The introductions include the materials used in the multilayer mirror, and rationale for the selection of materials, the shape and design of the target and the type of laser. At the same time, this article points out that the main problems for the EUVL are light debris reduction and the conversion efficiency improvement of EUV light.This paper also gives special analysis of the light source output devices of 13.5 nm EUVL machines produced by international famous companies——Gigaphoton of Japan and ASML of the Netherlands, which can generate more than 100 W level EUV power. Finally, this article summarizes and forecasts future research related to this technology. -
表 1 Gigaphoton公司EUV光源产品参数
Table 1. Specifications of Gigaphoton EUV system
Proto#1
Proof of ConceptProto#2
Key TechnologyPilot#1
HVM ReadyTarget Performance EUV power 25 W >100 W 250 W CE 3% 4.0% 5.0% Pulse Rate 100 kHz 100 kHz 100 kHz Output Angle Horizontal 62°upper 62°upper Availability ~1 week ~1 week >75% Technology Droplet Generator 20~25 μm < 20 μm < 20 μm CO2 Laser 5 kW 20 kW 27 kW Pre-pulse Laser Picosecond picosecond picosecond Collector Mirror Lifetime Test platform 10 days >3 months -
[1] 李小强.金宝搏188软件怎么用 辅助放电Sn等离子体13.5 nm极紫外辐射研究[D].哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2014.LI X Q. Research of 13.5 nm extreme ultraviolet radiation from tin plasma produced by laser-assisted discharge[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2014. (in Chinese) [2] HUTCHESON G D. Moore's law, lithography, and how optics drive the semiconductor industry[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2018, 10583: 1058303. doi: 10.1117/12.210341.full [3] PIRATI A, VAN SHOOT J, TROOST K, et al. The future of EUV lithography: enabling Moore's law in the next decade[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10143: 101430G. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4c04f740f379fcbd6ae165c8ce6fa31f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [4] DAVID A. Soft X-Rays and EUV Radiation[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2007: 17-20. [5] 楼祺洪, 袁志军, 张海波.光刻技术的历史与现状[J].科学, 2017, 69(3): 32-36. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kx201703008LOU Q H, YUAN ZH J, ZHANG H B. The history and present situation of lithography technology[J]. Science, 2017, 69(3): 32-36. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kx201703008 [6] LEVINSON H J. Principles of Lithography[M]. 3rd ed. Washington: SPIE Press, 2011: 47-50. [7] 万南. ASML出货新光刻机NXT2000i: 用于7nm/5nm DUV工艺[EB/OL]. (2018-08-03)[2019-02-02]. http://news.mydrivers.com/1/589/589237.htm.WAN N. ASML ships new lithography machine NXT2000i: for 7nm/5nm DUV process[EB/OL]. (2018-08-03)[2019-02-02]. http://news.mydrivers.com/1/589/589237.htm. (in Chinese) [8] 耿永友, 邓常猛, 吴谊群.极紫外光刻材料研究进展[J].红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程, 2014, 43(6): 1850-1856. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2014.06.027GENG Y Y, DENG CH M, WU Y Q. Recent progress of extreme ultraviolet resists[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2014, 43(6): 1850-1856. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2014.06.027 [9] 窦银萍, 孙长凯, 林景全.金宝搏188软件怎么用 等离子体极紫外光刻光源[J].中国光学, 2013, 6(1): 20-33. //www.illord.com/CN/abstract/abstract8894.shtmlDOU Y P, SUN CH K, LIN J Q. Laser-produced plasma light source for extreme ultraviolet lithography[J]. Chinese Optics, 2013, 6(1): 20-33. (in Chinese) //www.illord.com/CN/abstract/abstract8894.shtml [10] 张福昌, 李艳秋. EUV光刻中金宝搏188软件怎么用 等离子体光源的发展[J].微细加工技术, 2006(5): 1-7, 12. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wxjgjs200605001ZHANG F CH, LI Y Q. Development of laser produced plasma source for EUV lithography[J]. Microfabrication Technology, 2006(5): 1-7, 12. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wxjgjs200605001 [11] TICHENOR D A, RAY-CHAUDHURI A K, REPLOGLE W C, et al. System integration and performance of the EUV engineering test stand[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2001, 4343: 19-37. doi: 10.1117/12.436665 [12] MIURA T, MURAKAMI K, SUZUKI K, et al. Nikon EUVL development progress update[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2008, 6921: 69210M. doi: 10.1117/12.772444 [13] 芯智讯.从全球光刻机巨头ASML的成长史, 看中国半导体装备业的发展[EB/OL]. (2018-05-23)[2019-01-22]. http://www.icsmart.cn/19096/.XIN ZH X. Focusing on the development of China's semiconductor equipment industry from the growth history of global lithography company-ASML[EB/OL]. (2018-05-23)[2019-01-22]. http://www.icsmart.cn/19096/. (in Chinese) [14] 蔡懿, 王文涛, 杨明, 等.基于强金宝搏188软件怎么用 辐照固体锡靶产生极紫外光源的实验研究[J].物理学报, 2008, 57(8): 5100-5104. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3290.2008.08.069CAI Y, WANG W T, YANG M, et al. Experimental study on extreme ultraviolet light generation from high power laser-irradiated tin slab[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2008, 57(8): 5100-5104. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3290.2008.08.069 [15] CHEN H, WANG X B, DUAN L, et al. Angular distribution of ions and extreme ultraviolet emission in laser-produced tin droplet plasma[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2015, 117(19): 193302. doi: 10.1063/1.4921532 [16] 吴文娟.极紫外和软X射线窄带多层膜的研究[D].上海: 同济大学, 2007.WU W J. The study of extreme ultraviolet and Soft X-Ray narrowband multilayers[D]. Shanghai: Tongji University, 2007. (in Chinese) [17] BENSCHOP J, BANINE V, LOK S, et al. Extreme ultraviolet lithography: status and prospects[J]. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B: Microelectronics and Nanometer Structures Processing, Measurement, and Phenomena, 2008, 26(6): 2204-2207. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0227888465/ [18] 匡尚奇, 李硕, 杨海贵, 等.极紫外宽带多层膜反射镜离散化膜系的设计与制备[J].光学 精密工程, 2018, 26(10): 2395-2406. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201810007KUANG SH Q, LI SH, YANG H G, et al. Design and fabrication of EUV broadband multilayer mirrors with discrete thicknesses[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2018, 26(10): 2395-2406. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201810007 [19] BAJT S, ALAMEDA J B, BARBEE JR T W, et al. Improved reflectance and stability of Mo/Si multilayer[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2001, 4506: 65-75. doi: 10.1117/12.450946 [20] PELIZZO M G, SUMAN M, MONACO G, et al. High performance EUV multilayer structures insensitive to capping layer optical parameters[J]. Optics Express, 2008, 16(19): 15228-15237. doi: 10.1364/OE.16.015228 [21] FOMENKOV I. EUV source for high volume manufacturing: performance at 250 W and key technologies for power scaling (Keynote presentation)[R]. Dublin, Ireland, 2017. [22] KAWASUJI Y, NOWAK K M, HORI T, et al. Key components technology update of the 250 W high-power LPP-EUV light source[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10143: 101432G. [23] HENKE B L, GULLIKSON E M, DAVIS J C. X-ray interactions: photoabsorption, scattering, transmission, and reflection at E = 50-30, 000 eV, Z = 1-92[J]. Atomic Data and Nuclear Data Tables, 1993, 54(2): 181-342. doi: 10.1006/adnd.1993.1013 [24] BANINE V, BENSCHOP J P, LEENDERS M, et al. Relationship between an EUV source and the performance of an EUV lithographic system[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2000, 3997: 126-135. doi: 10.1117/12.390048 [25] SCHRIEVER G, MAGER S, NAWEED A, et al. Laser-produced lithium plasma as a narrow-band extended ultraviolet radiation source for photoelectron spectroscopy[J]. Applied Optics, 1998, 37(7): 1243-1248. doi: 10.1364/AO.37.001243 [26] 兰慧. Sn和SnO2靶金宝搏188软件怎么用 等离子体特性的研究[D].武汉: 华中科技大学, 2016.LAN H. Research on the characteristics of laser produced Sn and SnO2 plasma[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science & Technology, 2016. (in Chinese) [27] RAJYAGURU C, HIGASHIGUCHI T, KOGA M, et al. Parametric optimization of a narrow-band 13.5-nm emission from a Li-based liquid-jet target using dual nano-second laser pulses[J]. Applied Physics B, 2005, 80(4-5): 409-412. doi: 10.1007/s00340-005-1777-6 [28] NAGANO A, INOUE T, NICA P E, et al. Extreme ultraviolet source using a forced recombination process in lithium plasma generated by a pulsed laser[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2007, 90(15): 151502. doi: 10.1063/1.2719672 [29] TANAKA H, AKINAGA K, TAKAHASHI A, et al. Emission characteristics of EUV light source by CO2 laser-produced Xe and Sn plasma[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2004, 5448: 737-748. doi: 10.1117/12.547372 [30] HANSSON B A M, HERTZ H M. Liquid-jet laser-plasma extreme ultraviolet sources: from droplets to filaments[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2004, 37(23): 3233-3243. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/37/23/004 [31] CUMMINGS A, O'SULLIVAN G, DUNNE P, et al. Variable composition laser-produced Sn plasmas-a study of their time-independent ion distributions[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2004, 37(17): 2376-2384. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/37/17/006 [32] KIEFT E R, GARLOFF K, VAN DER MULLEN J J A M, et al. Comparison of experimental and simulated extreme ultraviolet spectra of xenon and tin discharges[J]. Physical Review E, 2005, 71(3): 036402. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.71.036402 [33] TOMIE T, AOTA T, UENO Y, et al. Use of tin as a plasma source material for high conversion efficiency[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2003, 5037: 147-155. doi: 10.1117/12.483751 [34] TAO Y, NISHIMURA H, OKUNO T, et al. Dynamic imaging of 13.5 nm extreme ultraviolet emission from laser-produced Sn plasmas[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2005, 87(24): 241502. doi: 10.1063/1.2139990 [35] SHIMADA Y, NISHIMURA H, NAKAI M, et al. Characterization of extreme ultraviolet emission from laser-produced spherical tin plasma generated with multiple laser beams[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2005, 86(5): 051501. doi: 10.1063/1.1856697 [36] YUSPEH S, SEQUOIA K L, TAO Y, et al. Optimization of the size ratio of Sn sphere and laser focal spot for an extreme ultraviolet light source[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 93(22): 221503. doi: 10.1063/1.3036956 [37] HARILAL S S, SIZYUK T, SIZYUK V, et al. Efficient laser-produced plasma extreme ultraviolet sources using grooved Sn targets[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2010, 96(11): 111503. doi: 10.1063/1.3364141 [38] CUMMINS T, O'GORMAN C, DUNNE P, et al. Colliding laser-produced plasmas as targets for laser-generated extreme ultraviolet sources[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 105(4): 044101. doi: 10.1063/1.4891762 [39] BÖWERING N R, FOMENKOV I V, BRANDT D C, et al. Performance results of laser-produced plasma test and prototype light sources for EUV lithography[J]. Journal of Micro/Nanolithography, MEMS, and MOEMS, 2009, 8(4): 041504. doi: 10.1117/1.3224942 [40] MIZOGUCHI H, NAKARAI H, ABE T, et al. Performance of one hundred watt HVM LPP-EUV source[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2015, 9422: 94220C. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=CC0215024557 [41] WHITE J, DUNNE P, HAYDEN P, et al. Optimizing 13.5 nm laser-produced tin plasma emission as a function of laser wavelength[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2007, 90(18): 181502. doi: 10.1063/1.2735944 [42] AOTA T, NAKAI Y, FUJIOKA S, et al. Characterization of extreme ultraviolet emission from tin-droplets irradiated with Nd:YAG laser plasmas[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2008, 6921: 69212T. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/112/4/042064 [43] ANDO T, FUJIOKA S, NISHIMURA H, et al. Optimum laser pulse duration for efficient extreme ultraviolet light generation from laser-produced tin plasmas[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 89(15): 151501. doi: 10.1063/1.2361260 [44] HARILAL S S, TILLACK M S, TAO Y, et al. Extreme-ultraviolet spectral purity and magnetic ion debris mitigation by use of low-density tin targets[J]. Optics Letters, 2006, 31(10): 1549-1551. doi: 10.1364/OL.31.001549 [45] BANINE V Y, KOSHELEV K N, SWINKELS G H P M. Physical processes in EUV sources for microlithography[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2011, 44(25): 253001. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/44/25/253001 [46] ENDO A, ABE T, HOSHINO H, et al. CO2 laser-produced Sn plasma as the solution for high-volume manufacturing EUV lithograph[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2007, 6703: 670309. doi: 10.1117/12.732254 [47] ENDO A, KOMORI H, UENO Y, et al. Laser-produced plasma source development for EUV lithography[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2009, 7271: 727108. doi: 10.1117/12.813639 [48] FUJIOKA S, SHIMOMURA M, SHIMADA Y, et al. Pure-tin microdroplets irradiated with double laser pulses for efficient and minimum-mass extreme-ultraviolet light source production[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 92(24): 241502. doi: 10.1063/1.2948874 [49] FREEMAN J R, HARILAL S S, VERHOFF B, et al. Laser wavelength dependence on angular emission dynamics of Nd:YAG laser-produced Sn plasmas[J]. Plasma Sources Science and Technology, 2012, 21(5): 055003. doi: 10.1088/0963-0252/21/5/055003 [50] LETARDI T, LO D, ZHENG C E. Particle dynamics of debris produced during laser-plasma soft X-ray generation[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2001, 89(2): 1458-1462. doi: 10.1063/1.1334365 [51] YANAGIDA T, NAGANO H, WADA Y, et al. Characterization and optimization of tin particle mitigation and EUV conversion efficiency in a laser produced plasma EUV light source[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2011, 7969: 79692T. doi: 10.1117/12.879189 [52] NⅡMI G, UENO Y, NISHIGORI K, et al. Experimental evaluation of a stopping power of high-energy ions from a laser-produced plasma by a magnetic field[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2003, 5037: 370-377. doi: 10.1117/12.483747 [53] HARILAL S S, O'SHAY B, TAO Y, et al. Ion debris mitigation from tin plasma using ambient gas, magnetic field and combined effects[J]. Applied Physics B, 2007, 86(3): 547-553. doi: 10.1007/s00340-006-2532-3 [54] SUN Y B, LIN J Q, GAO X, et al. Characteristics of ion debris from laser-produced tin plasma and mitigation of energetic ions by ambient gas[J]. Science China Physics, Mechanics and Astronomy, 2012, 55(3): 392-395. doi: 10.1007/s11433-012-4644-6 [55] MIZOGUCHI H, NAKARAI H, ABE T, et al. Performance of one hundred watt HVM LPP-EUV source[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2015, 9422: 94220C. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=CC0215024557 [56] 尹志坚. EUV光刻机: ASML 2018年总销量18台, 计划明年30台[EB/OL]. (2019-01-25)[2019-02-22]. http://www.elecfans.com/d/858465.html. YIN ZH J. EUV lithography machine: total sales of ASML EUV lithography machine is 18 in 2018, and that number is projected to increase to 30 in 2019[EB/OL]. (2019-01-25)[2019-02-22]. http://www.elecfans.com/d/858465.html. (in Chinese) [57] 旺材芯片. ASML今年将推新一代EUV光刻机NXE: 3400C产能170片/小时[EB/OL]. (2019-01-25)[2019-02-22]. https://www.xianjichina.com/special/detail_382932.html.WANG C X P. ASML will push a new generation of EUV lithography machine NXE this year: 3400C capacity 170 pieces/hour[EB/OL]. (2019-01-25)[2019-02-22]. https://www.xianjichina.com/special/detail_382932.html. (in Chinese) [58] MIZOGUCHI H, NAKARAI H, ABE T, et al. High power LPP-EUV source with long collector mirror lifetime for high volume semiconductor manufacturing[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2018, 10583: 1058318. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=f8eff57ec8ecff5479d1b3b2737f1fcf&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [59] NOWAK K M, OHTA T, SUGANUMA T, et al. Multiline short-pulse solid-state seeded carbon dioxide laser for extreme ultraviolet employing multipass radio frequency excited slab amplifier[J]. Optics Letters, 2013, 38(6): 881-883. doi: 10.1364/OL.38.000881 [60] NOWAK K M, OHTA T, SUGANUMA T, et al. Spectral characteristics of quantum-cascade laser operating at 10.6 μm wavelength for a seed application in laser-produced-plasma extreme UV source[J]. Optics Letters, 2012, 37(22): 4765-4767. doi: 10.1364/OL.37.004765 [61] MIZOGUCHI H, NAKARAI H, ABE T, et al. Performance of 250 W high-power HVM LPP-EUV source[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10143: 101431J. doi: 10.1117/12.2256652.full [62] YOICHI T, TATSUYA Y, JUNICHI N, et al. Efficient pulse amplification using a transverse-flow CO2 laser for extreme ultraviolet light source[J]. Optics Letters, 2012, 37(16):3300. doi: 10.1364/OL.37.003300 [63] PIRATI A, PEETERS R, SMITH D, et al. EUV lithography performance for manufacturing: status and outlook[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2016, 9776: 97760A. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/299644651_EUV_lithography_performance_for_manufacturing_status_and_outlook?ev=auth_pub [64] 徐明飞, 庞武斌, 徐象如, 等.高数值孔径投影光刻物镜的光学设计[J].光学 精密工程, 2016, 24(4): 740-746. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201604008XU M F, PANG W B, XU X R, et al. Optical design of high-numerical aperture lithographic lenses[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2016, 24(4): 740-746. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201604008 [65] 中国电子报社.解决集成电路"掐脖子"问题, 光刻机这篇文章怎么做?[EB/OL].(2018-07-12)[2019-03-26]. http://www.sohu.com/a/240821218_464075.CHINA ELECTRONIC NEWSPAPER. To solve the "neck pinching" problem of integrated circuits, what should photolithography do?[EB/OL]. (2018-07-12)[2019-03-26]. http://www.sohu.com/a/240821218_464075. (in Chinese) [66] 半导体行业联盟.国产22 nm光刻机, 可制造10纳米芯片![EB/OL]. (2018-11-30)[2019-02-26]. http://www.sohu.com/a/278788826_756356.SEMICONDUCTOR INDUSNY ALLIANCE. Domestic 22nm lithography machine can manufacture 10 nanometer chips![EB/OL]. (2018-11-30)[2019-02-26]. http://www.sohu.com/a/278788826_756356. (in Chinese) -





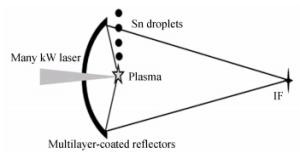
 下载:
下载: